Researchers develop new generation NIR-II dyes for biomedical imaging
Near-infrared window-II (NIR-II, 1000-1700 nm) fluorescence imaging has recently emerged as the frontrunner in molecular imaging and translational research.
Donor-acceptor-donor (D-A-D) type organic fluorophores generally exhibit good biocompatibility, and tunable optical properties, which have been widely used in biological imaging. However, most of the research focused on the donor part development and much less attention has been focused on the acceptor part.
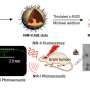
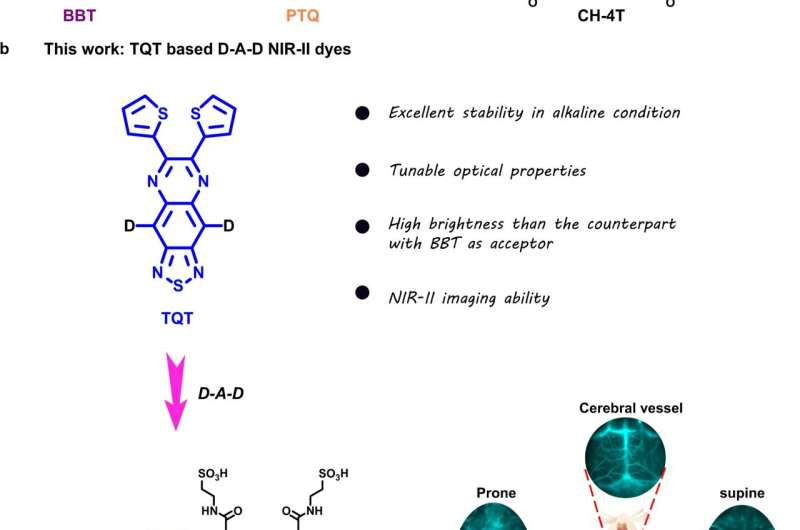
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers led by Cheng Zhen and Chen Hao from the Molecular Imaging Center of Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a novel water-soluble NIR-II dye, FT-TQT, for versatile biomedical imaging applications, which is based on a new electron acceptor, 6,7-di(thiophen-2-yl)-[1,2,5] thiadiazolo[3,4-g] quinoxaline (TQT).
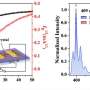
Compared with traditional electron acceptors, benzobisthiadiazole (BBT) and 6,7-diphenyl-[1,2,5] thiadiazolo[3,4-g]quinoxaline (PTQ), TQT shows much higher stability in alkaline conditions than BBT and a 50 nm longer bathochromic shift in the absorption spectrum than PTQ.
Furthermore, TQT-based D-A-D dyes show ultra-high stability under reactive oxygen species/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS), metal ions, active biomolecules, and various alkaline conditions.
In addition, TQT-based D-A-D dye, FT-TQT, demonstrates real-time cerebral and tumor vessel imaging capability. NIR-II fluorescence imaging achieves dynamic monitoring of tumor vascular disruption after treatment with combretastatin A4 phosphate (CA4P).
This study offers a promising molecular design strategy to develop new NIR-II fluorophores. Also, it provides a valuable tool to monitor and evaluates vascular-related disease treatment.
More information: Aiyan Ji et al, Acceptor engineering for NIR-II dyes with high photochemical and biomedical performance, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31521-y