Childhood health equity: The urgent need to do things differently—now
Despite years of research, discussions and advocacy in relation to nurturing children's development through healthy eating and active living, there's been very little in the way of progress—sugary drinks are still advertised prolifically, there's hidden salt and sugar in foods, and most kids spend more time in front of screens rather than outside.
It's time for the chatter to stop, and for effective interventions to be put in place.
Why? Because fostering the growth, development, health and well-being of children is a global priority, and the early childhood period presents a critical window to influence lifelong trajectories.
The formative years from conception to age five (also known as the first 2000 days) provide multiple teachable "moments" for both the child and their family to establish and reinforce healthy lifestyle behaviors that can persist throughout childhood, and into adolescence and adulthood.
Recently, Dr. Rachael Green and I formed the International Healthy Eating Active Living Matters (HEALing Matters) Alliance, a global network of academics, practitioners, and policymakers working across child health and development, with the goal of improving health equity for children and their families. We recently published a policy paper in the journal, Health & Social Care in the Community.
Our alliance goal is aligned with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development—released by the United Nations in 2015—aiming for all children to have the best start in life, irrespective of where they're born, their ethnicity, and cultural heritage.
Unfortunately, the pursuit of this goal has been siloed across community, health, and education sectors in different countries and regions, leading to a fractured response at best, with many families and their children falling through the cracks.
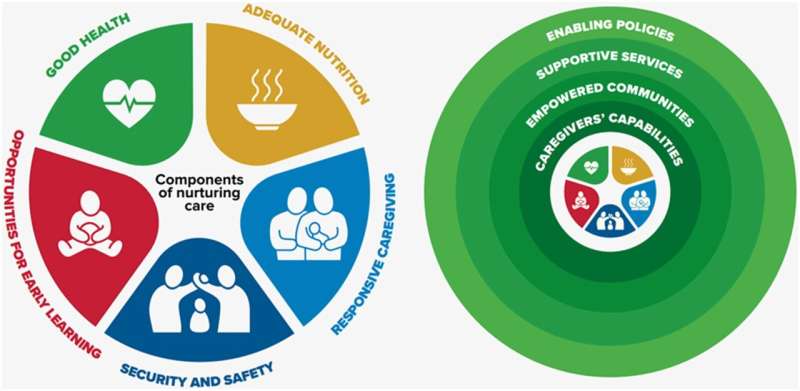
Essential to achieving the best start in life for all children is a focus on supporting families to nurture their young children's growth and development through healthy eating and active living within the context of responsive caregiving, safety and security, and opportunities for early learning.
In The Lancet's 2017 series on Advancing Early Childhood Development, the absence of nurturing care was identified as a primary reason why children don't thrive. This is often the result of structural disadvantage, not individual choice, reinforcing the need to address the underlying social and physical conditions that prevent parents and families from providing nurturing care.
The COVID-19 impact
Globally, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed and highlighted the structural drivers of health inequalities, and exacerbated existing social vulnerabilities.
As such, the need to do things differently is now urgent. Here lies a window of opportunity for all governments to facilitate collective action through the co-design and delivery of programs and services that foster the strengths and resilience of children, families and communities across the first 2000 days.
The development of initiatives in active consultation and engagement with the community will ensure they're relevant to the needs of the target population.
We also recommend that financial investment is made by all governments to ameliorate poverty, income inequality, and food insecurity associated with racial inequality, and that we must transform the way we work together for better child outcomes.
The alliance brings together the world's best minds in the fields of child growth (operationalized as healthy weight gain from birth to age five) and development, and implementation science.
Rather than knowing the "what" alone about child disadvantage, we also need to know the "how" we can best work together to support early child growth and development.
Working toward a holistic approach
Knowing how to best work together necessarily means understanding how health, social care/community services and early childhood education organizations can advance and resource a holistic, person-centered approach to support and enable parents to nurture their children's development through healthy eating and active living in a collaborative, multi-sectoral way.
These are the sectors that have the most contact with children and families from pregnancy to age five years. To achieve this collective action, we need systems change driven by advanced, theoretically-informed implementation science.
With the goal of breaking down silos and offering a more coordinated approach, we argue that nurturing children's development through healthy eating and active living in the context of responsive emotional support, safety, and early learning must occur through multi-sectoral collaborations that foster positive developmental trajectories by mitigating adversities when necessary.
And we argue the time to act genuinely and effectively, to ensure all children have the best start in life, is now.
The study is published in the journal Health & Social Care in the Community.
More information: Helen Skouteris et al, Nurturing children's development through healthy eating and active living: Time for policies to support effective interventions in the context of responsive emotional support and early learning, Health & Social Care in the Community (2022). DOI: 10.1111/hsc.14106
The Lancet series: nurturing-care.org/lancet-adva … om-science-to-scale/