This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
App helps promote better dietary habits and less screen time in young children
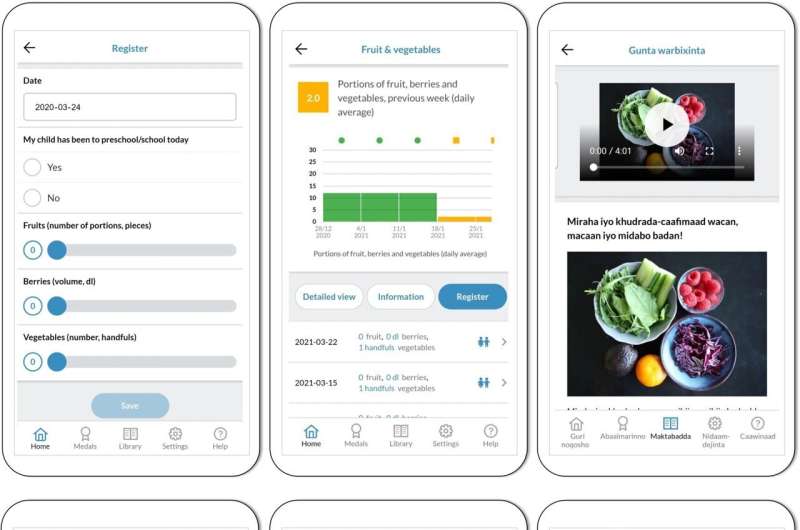
With the help of a multi-language smartphone app, parents in Sweden were able to give their young children better dietary habits and less screen time, a study by researchers from Karolinska Institutet published in the International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity reports.
Overweight and obesity in children is a growing problem in the world. In Sweden, 11 percent of four-year-olds are overweight. The corresponding figure for six to nine-year-olds is 21 percent. In socioeconomically deprived areas, childhood overweight is even more widespread.
"One important and unique aspect of the study is that the app is available in many languages, including Swedish, Somali, Arabic and English, to reach as many families as possible," says the study's last author Marie Löf, professor at the Department of Biosciences and Nutrition, Karolinska Institutet.
To test their newly designed smartphone app, MINISTOP 2.0, the researchers recruited a total of 552 families with a child between the ages of thirty months and three years from 19 child healthcare centers around Sweden. Twenty-four percent of the children in the study had two foreign-born parents, corresponding to the national percentage. Half of the children were randomly assigned to a control group that received standard care, half to the intervention group that used the app.
The habits of the children were documented
For the six months of the study, the parents of the children in the intervention group were able to use the app to receive comprehensive information and support for behavior change, as well as record their child's consumption of fruit, vegetables, sweet and salty snacks, and sweetened drinks and get feedback. They were also able to register their child's physical activity and screen time.
"The paper shows that the children in the intervention group had a statistically significant consumption of sweets, snacks and sugared drinks, and less screen time," says the study's first author Christina Alexandrou, doctoral student affiliated with the same department.
For example, the weight of sweetened drinks consumed was 32 grams lower a day in the intervention group than in the control group, which equates to a 20 percent or so reduction in average consumption amongst Swedish preschool children.
"It was also nice to see that the parents who'd had access to the app reported a greater sense of self-efficacy in their ability to promote healthy lifestyles in their child with respect to diet and exercise," says Professor Löf, who continues:
"The results are valuable to the child healthcare services in their health-promotion activities. We've shown that by using a digital tool we can make a difference, and the app will now be implemented at several child healthcare clinics in Sweden. In reaching many families, regardless of language, we can contribute to healthier lifestyles in young children and help parents feel validated in their parenting in this regard."
More information: Christina Alexandrou et al, Effectiveness of a Smartphone App (MINISTOP 2.0) integrated in primary child health care to promote healthy diet and physical activity behaviors and prevent obesity in preschool-aged children: randomized controlled trial, International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s12966-023-01405-5