This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New options for treating eczema
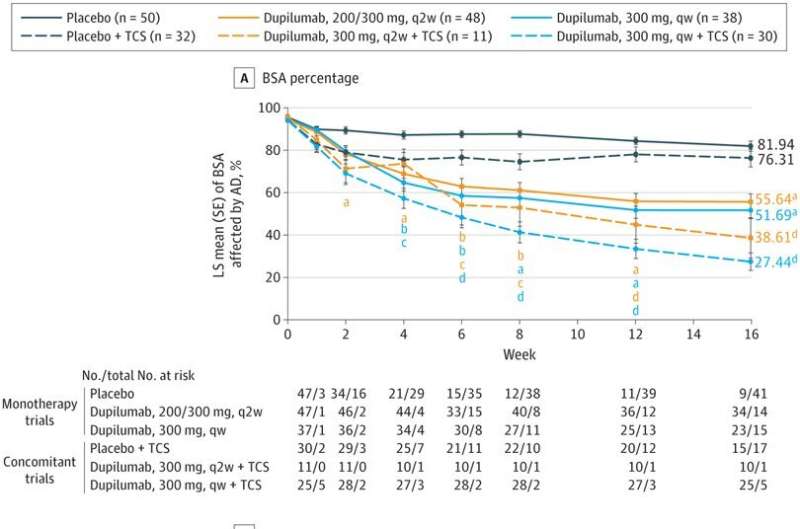
Patients with severe eczema who were treated with the drug dupilumab experienced a reduction in symptoms and improved quality of life, according to a meta-analysis of several clinical trials published in JAMA Dermatology.
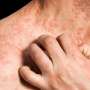
The findings suggest dupilumab is a safe, effective treatment for cases of erythrodermic atopic dermatitis, or eczema, in which more than 90% of the body was affected.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the most common type of eczema, affecting more than 9.6 million children and about 16.5 million adults in the U.S., according to the National Eczema Association.
In the current study, investigators analyzed 209 patients with erythrodermic AD in six clinical trials. Patients given dupilumab treatment saw early and significant improvement of symptoms, including decreased itchiness and lower levels of atopic dermatitis biomarkers. Patients treated with dupilumab also reported a higher quality of life and fewer symptoms of anxiety or depression, according to the study.
"The question we have for many new therapies is, 'Will this work for the most severe patients?'" said Amy Paller, MD, the chair and Walter J. Hamlin Professor of Dermatology and a co-author of the study. "This group has the greatest risk for infection, comorbidities and even morbidity. So, we looked at the most severe patients, and the bottom line is they respond just as well to the treatment as milder cases."
Previously, treatment for AD has consisted of general immunosuppressant medications, Paller said. Because dupilumab is specifically targeted to block the cytokines responsible for inflammatory responses, it is generally considered safer for long-term use.
Side effects reported in the study included injection-site reaction, conjunctivitis and nasopharyngitis. Patients with erythrodermic AD were more likely to develop conjunctivitis compared to patients with milder cases, according to the study.
"I think we're just at the very beginning of having many options for our patients with atopic dermatitis," Paller said. "The reason that this research with this most severe group is important is that it gives us some insight into the neediest patients, the ones who are most severe. It also tells us that this group, although they will do very well, may have a higher risk for conjunctivitis. So, we must be on the lookout for it."
More information: Amy S. Paller et al, Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Patients With Erythrodermic Atopic Dermatitis, JAMA Dermatology (2023). DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.6192