This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Assessing the impact of health literacy on medication adherence among Black Medicaid beneficiaries with hypertension
A new study showed that lower health literacy was significantly associated with lower adherence to medication among Black Medicaid beneficiaries with hypertension in Delaware. The study, with additional findings, is published in Population Health Management.
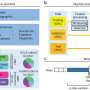
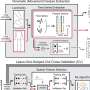
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can be attributed to nonadherence to antihypertensive medication. In the current study by Michael Butzner, DrPH, MPH, from the Pennsylvania State College of Medicine, and co-authors, a major finding was that less than half of participants received an appropriate prescription for treatment and most patients were non-adherent.
An estimated 40% of American adults have limited health literacy, and racial and ethnic minorities are disproportionately affected by limited and low health literacy.
The investigators reported that men, younger adults, increased time enrolled in Medicaid over the study period, and basic health literacy were significantly associated with low adherence to medication.
"The current study highlights the necessity of providing literacy assistance and health education to promote healthy behaviors and lifestyle change such as medication adherence," stated the investigators.
"Sadly, researchers have demonstrated that less than 25% of all patients actually take the drugs doctors prescribe for them—a number that has been stable for three decades. Dr. Butzner has helped to further clarify this dilemma, and he has reinforced our challenge to focus on health literacy as a key factor in non-adherence to medication," says David Nash, MD, MBA, Editor-in-Chief of Population Health Management.
More information: Michael Butzner et al, Impact of Health Literacy on Medication Adherence Among Black Medicaid Beneficiaries with Hypertension in Delaware: A Cross-Sectional Study, Population Health Management (2023). DOI: 10.1089/pop.2022.0270