This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Different areas of the brain activated depending on structural complexity of music and language, study shows

Distinct, though neighboring, areas of the brain are activated when processing music and language, with specific sub-regions engaged for simple melodies versus complex melodies, and for simple versus complex sentences, according to research from UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by co-first authors Meredith McCarty, Ph.D. candidate in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and Elliot Murphy, Ph.D., postdoctoral research fellow in the department, was published recently in iScience. Nitin Tandon, MD, professor and chair ad interim of the department in the medical school, was senior author.
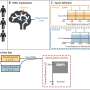
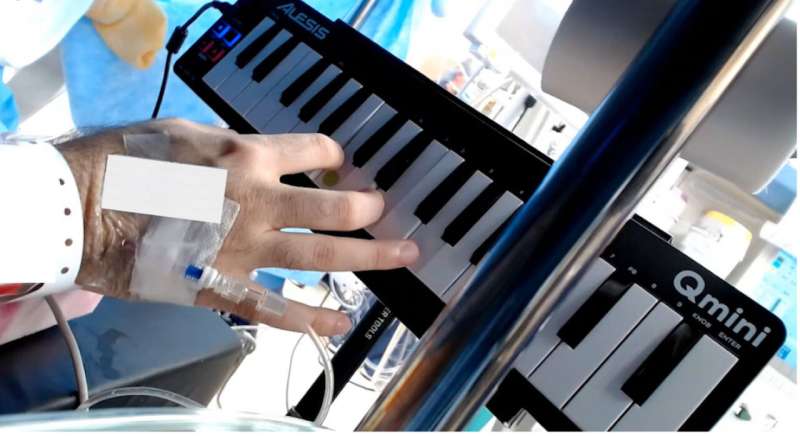
The research team used the opportunity provided during an awake craniotomy on a young musician with a tumor in the brain regions involved in language and music. The patient heard music and played a mini-keyboard piano to map his musical skills, heard and repeated sentences and heard descriptions of objects that he then named to map his language. Musical sequences were melodic or not melodic and differed in complexity, while auditory recordings of sentences differed in syntactic complexity.
Direct brain recordings with electrodes placed on the brain surface mapped out the location and characteristics of brain activity during music and language. Small currents were passed into the brain to localize regions critical for language and music perception and production.
"This allowed us not just to obtain novel insights into the neurobiology of music in the brain, but to enable us to protect these functions while performing a safe, maximal resection of the tumor," said Tandon, the Nancy, Clive and Pierce Runnels Distinguished Chair in Neuroscience of the Vivian L. Smith Center for Neurologic Research and the BCMS Distinguished Professor in Neurological Disorders and Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School and a member of the Texas Institute for Restorative Neurotechnologies (TIRN) at UTHealth Houston.
"If we look purely at basic brain activation profiles for music and language, they often look pretty similar, but that's not the full story," said McCarty, who is also a graduate research assistant at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center UTHealth Houston Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences and a member of TIRN. "Once we look closer at how they assemble small parts into larger structures, some striking neural differences can be detected."
Language and music involve the productive combination of basic units into structures. However, researchers wanted to study whether brain regions sensitive to linguistic and musical structure are co-localized, or exist in the same physical space.
"The unparalleled, high resolution of intracranial electrodes allows us to ask the kinds of questions about music and language processing that cognitive scientists have long awaited answers for, but were unable to address with traditional neuroimaging methods," said Murphy, a member of TIRN. "This work also truly highlights the generosity of patients who work closely with researchers during their stay at the hospital."
Overall, they found shared temporal lobe activity for music and language, but when examining features of melodic complexity and grammatical complexity, they discovered different temporal lobe sites to be engaged. Therefore, music and language activation at the basic level is shared, however when the researchers examined comparing basic melodies vs. complex melodies, or simple sentences versus complex sentences, different areas show distinct sensitivities.
Specifically, cortical stimulation mapping of the posterior superior temporal gyrus (pSTG) disrupted music perception and production, along with speech production. The pSTG and posterior middle temporal gyrus (pMTG) activated for language and music. While pMTG activity was modulated by musical complexity, pSTG activity was modulated by syntactic complexity.
Tandon resected the patient's mid-temporal lobe tumor at Memorial Hermann-Texas Medical Center. At his four-month follow-up, the patient was confirmed to have fully preserved musical and language function, without evidence of deterioration.
More information: Meredith J. McCarty et al, Intraoperative cortical localization of music and language reveals signatures of structural complexity in posterior temporal cortex, iScience (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107223