This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
MS: Mouse model suggests inflammation in meninges may spill over to into gray matter
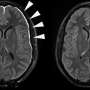
A study in mice suggests that inflammation in the brain's barrier, the meninges, may spill over into gray matter and cause changes that can contribute to progressive multiple sclerosis (MS).
The research, published in eLife, is described as an important study that advances our understanding of the mechanisms of brain damage in this autoimmune disease. It involves the use of novel methods to provide what they say is convincing evidence for a gradient of immune genes and inflammatory markers from the meninges to the adjacent brain tissue in mice.
Inflammation within the meninges is found in all types of MS. There is mounting evidence to suggest this inflammation plays a pivotal role in the progression of the disease, including loss of the protective coating on nerves (demyelination), loss of new nerve sprouts (neurites) and decreased volume of gray matter.
"Gray matter injury is linked to disabling MS symptoms like cognitive dysfunction and depression," explains Sachin Gadani, a neuroimmunology fellow at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, US, and a co-first author of the study alongside Saumitra Singh, Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
"Meningeal inflammation appears to be a critical driver of cortical gray matter pathology, but attempts to characterize the mechanism in an unbiased manner have been limited by the absence of spatially resolved data—that is, critical information about the anatomical relationship between meningeal inflammation and the underlying brain tissue. We set out to determine the patterns of gene activity in the meninges and the surrounding gray matter, while preserving the context about the position of those cells in the brain."
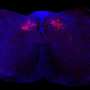
Gadani, Singh and colleagues used an approach called spatial transcriptomics, whereby the pattern of gene activity in a tissue is measured and the information is then pieced back together to show the pattern of gene activity in the original location. They started by measuring gene activity in the inflamed meninges in a mouse model of MS against the meninges in healthy mice, and then compared this to the expression of genes in the surrounding gray matter in both groups of mice.
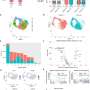
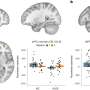
As the team expected, they found an increased expression (upregulation) of genes related to immune cells and pathways, immune cell infiltration, and the activation of brain-specific immune cells called microglia. To understand more about the proximity of this gene activity to the meningeal region, they analyzed patterns of gene activity along a path from the meninges to the thalamus.
All the groups of genes declined in activity with increasing distance from the inflamed meningeal region. However, some genes showed a more gradual decline—particularly those involved in immune processes such as antigen processing and presentation. This suggests that some upregulation of pro-inflammatory genes had spilled over from the brain's meningeal region into the gray matter.
"This is the first time a study has characterized a mouse model of meningeal inflammation and gray matter injury using spatial transcriptomics," says co-first author Saumitra Singh. "We've provided a publicly available dataset from our work that we hope others can use in future research."
A limitation of this study is that the spatial resolution may not be sufficient to distinguish between the meninges and surrounding gray matter with certainty. Additionally, while the authors used a mouse model that represents many pathological features of MS, it does not fully represent human disease, and the analysis does not consider different timepoints in the development of MS. Despite this, the authors say their findings could pave the way for future studies using human samples.
"Our findings have revealed several candidate pathways in the development of gray matter injury. Future work should focus on spatial transcriptomics in human samples which, thanks to advances in technology, is now becoming more feasible," concludes senior author Pavan Bhargava, Associate Professor of Neurology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
More information: Sachin P. Gadani et al, Spatial Transcriptomics of Meningeal Inflammation Reveals Variable Penetrance of Inflammatory Gene Signatures into Adjacent Brain Parenchyma, (2023). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.88414.1