This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers discover that skin keratinocytes are involved in warm temperature sensation
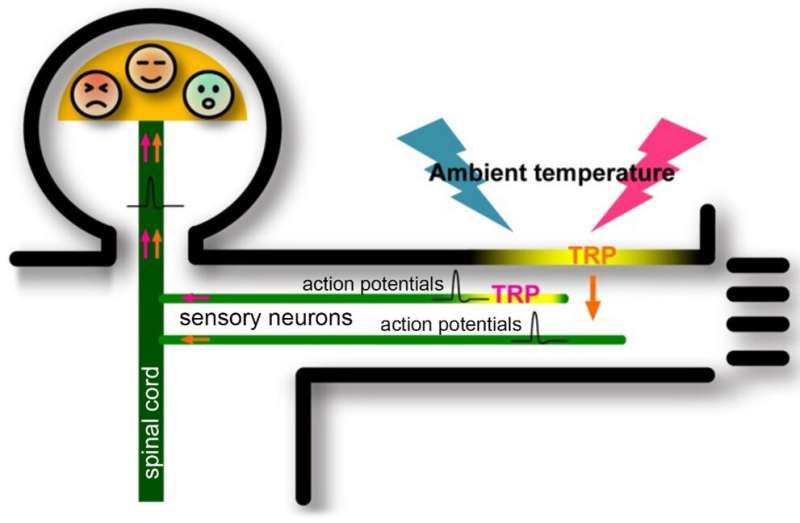
Sensory neurons play a crucial role in the perception of "hot" and "cold". They express a group of ion channels called thermosensitive TRP channels. For example, TRPV1 (activated above 43°C) and TRPM8 (activated below 29°C) send the "hot" and "cold" information to our brains, respectively, for which the 2021 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded.
However, TRPV3, which is activated by warm temperatures (32–39°C), is rarely detected in sensory neurons but is abundantly expressed in the skin keratinocytes. Although the concept that not only sensory neurons but also skin keratinocytes sense temperature has been proposed, there was a big controversy. It is also not concluded whether the response of TRPV3 in epidermal tissue is able to be transmitted to the brain and elicits temperature sensation.
In this study, the research group focused on TMEM79, a protein that is expressed in skin keratinocytes similar to TRPV3 but whose function is not well understood, in order to investigate the function of TRPV3. The research is published in the journal Nature Communications.
First, the research group overexpressed TRPV3 and TMEM79 in HEK293T cells and examined the TRPV3-mediated current responses. They found that the TRPV3-mediated currents were smaller in the cells co-expressing TMEM79 and TRPV3 than in cells expressing TRPV3 alone. This result indicates that TMEM79 reduces TRPV3-mediated currents.
Then, the research group made TMEM79-deficient mice, and examined the temperature-dependent behaviors using Thermal Gradient Ring with a donut shape. When they made a floor temperature gradient of from 10 to 45°C in the 25°C room temperature condition, wild-type mice preferred about 30.4°C. While TMEM79-deficient mice rapidly moved to warmer temperature of 34.4°C. This suggests that mouse temperature sensation is affected by the changes in TRPV3-mediated currents in the skin upon loss of TMEM79.TRPV3-mediated currents were indeed larger in the skin keratinocytes lacking TMEM79 than in those of wild-type mice.
This shows that TRPV3-mediated currents were inhibited by TMEM79 in the normal condition and that TRPV3-mediated currents were increased without TMEM79.
Finally, the research group examined how co-expression of TRPV3 and TMEM79 causes reduction of TRPV3-mediated currents in the skin keratinocytes. TRPV3 proteins which are normally expressed in the plasma membrane moved to cytosolic space upon co-expression of TMEM79. In other words, reduction of the amount of TRPV3 proteins on the plasma membrane decreased TRPV3-mediated currents.
In addition, it was found that TRPV3 proteins were carried to the lysosomes with TMEM79, followed by TRPV3 degradation, which is consistent with the reduction in the total TRPV3 proteins in the cell upon co-expression of TMEM79. Furthermore, the research group found that TRPV3 makes a physical complex with TMEM79 on the plasma membrane.
The research group concluded that temperature sensitivity in the skin is controlled by the regulation of the amount of TRPV3 proteins upon binding with TMEM79 in the skin keratinocytes. These results put an end to the long-standing controversy regarding the possible involvement of skin keratinocytes in temperature detection. This could lead to the development of a way to control our temperature sensation by regulating the function of TRPV3 or TMEM79.
More information: Jing Lei et al, Involvement of skin TRPV3 in temperature detection regulated by TMEM79 in mice, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39712-x