August 2, 2023 report
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Implanted cells triggered by electricity used to drive in vivo gene expression
Two significant factors have hampered the age of human-integrated cybernetics. One, humans can interact well with electronic devices without needing to implant them. Nearly all cybernetic human-machine interactions can be operated at the touch of a finger, except in a subset of medically necessary cases.
Two, the biological human machinery at a cellular and genomic level is simply more advanced at operating a biological lifeform than anything humans create. Having biologically supported tech incorporated into a human body, based on current technology, would be a downgrade.
A new vision of cybernetics is beginning to emerge, where tech plays a supporting role, and human genetics drive the changes. Researchers at ETH Zürich in Switzerland have found a way to harness the power of genetic expression using a novel current technology.
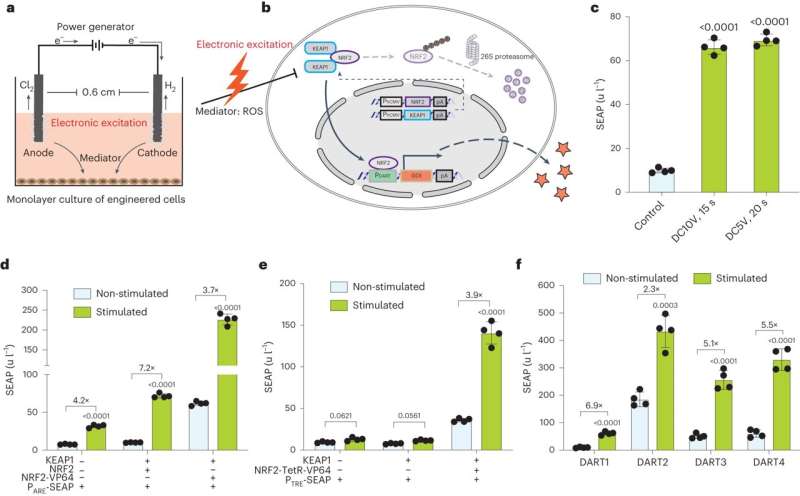
In a paper, "An electrogenetic interface to program mammalian gene expression by direct current," published in Nature Metabolism, the team detail an electro-genetic interface called Direct Current Actuated Regulation Technology (DART), enabling time and voltage-dependent transgene expression in human cells using direct current (DC) from batteries.
DART generates controlled levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS form through electron-transfer reactions during cellular respiration in mitochondria, peroxisomes, and NADPH oxidase in immune cells during immune responses. KEAP1, a critical tumor and metastasis suppressor, is also a native ROS detector.
KEAP1 confines NRF2, a nuclear factor linked to antioxidative defenses, for degradation. When ROS levels surge, KEAP1 releases NRF2, which moves to the nucleus, connecting with antioxidant-response elements to orchestrate antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses.
In a proof-of-concept study using a diabetic mouse model, transdermal stimulation of engineered human cells with energized acupuncture needles via DART resulted in insulin release and restored normal blood glucose levels.
Engineered cells were microencapsulated and implanted subcutaneously in mice. Microencapsulation was utilized to protect the cells from the host immune system while allowing nutrients and therapeutic proteins to diffuse freely. Electrostimulation of the implanted microencapsulated cells by acupuncture needles was tested at different voltage levels and battery types, including AAA batteries, AA batteries, 9V blocks, and button cells.
A single daily electrostimulation of implanted engineered cells at 4.5 V for 10 seconds triggered the production and release of sufficient insulin to restore normoglycemia in experimental mouse type 1 diabetes, comparable to long-acting insulin therapies that can maintain relatively stable blood-sugar levels for 24 hours.
Designed with safety in mind, DART uses low-voltage DC sources (~4.5 V), operates with minimal energy requirements (10 seconds, once per day), and uses acupuncture needle electrodes already approved by the World Health Organization and US Food and Drug Administration. In a hypothetical consumer use application, the most limiting factor might be access to three AAA batteries with 10 seconds' worth of charge left or, in a pinch, a cell phone charger.
While still at the discovery stages of development, the future of DART technology could facilitate wearable devices for direct gene-based therapies and metabolic interventions.
According to the paper authors, "it should be straightforward to link DART control to the in situ production and dosing of a wide range of biopharmaceuticals. We believe simple electrogenetic interfaces such as DART that functionally interconnect analog biological systems with digital electronic devices hold great promise for a variety of future gene and cell-based therapies, including closed-loop genetic interventions, real-time dosing and global telemetric monitoring by medical staff or algorithms."
More information: Jinbo Huang et al, An electrogenetic interface to program mammalian gene expression by direct current, Nature Metabolism (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00850-7
© 2023 Science X Network