This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New research sheds light on the side effects of COVID-19 vaccination
Immediately after COVID-19 vaccination, Danes experienced side effects such as malaise, fever and fatigue. Serious side effects such as facial paralysis and allergic reactions are rare, but 30% of menstruating women reported changes in their menstrual cycle.
Two new studies on the side effects of COVID-19 vaccination have just been published by Aarhus University.
Both studies are based on the Danish BiCoVac cohort, which makes it possible to carry out studies based on a large group of the Danish population.
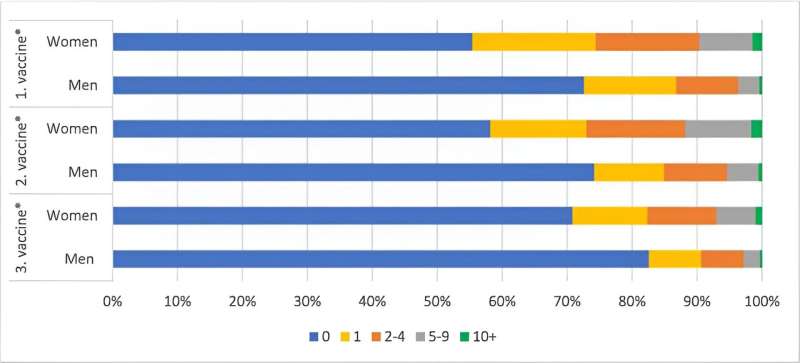
One of the studies, published in Vaccine, examined the acute side effects of COVID-19 vaccination.
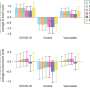
The most frequently reported side affects after the first small prick on the shoulder are redness and pain at the injection site, which 20% of people experience. After the second and third jabs, fatigue is the most reported side effect—reported by 22% and 14% of people, respectively.
The study found that common side effects such as malaise, fever and fatigue are among the most frequently reported in Denmark after COVID-19 vaccination. More serious side effects such as facial paralysis and allergic reactions are not as common.
"Women, people between the ages of 25-35 and people who had COVID-19 prior to being vaccinated reported experiencing side effects more frequently than men, the elderly and people who had not previously had COVID-19," says Kristoffer Torp Hansen, first author of the study and research assistant at the Department of Public Health.
The results also show that the acutely occurring side effects differ depending on which vaccine is administered.
People vaccinated with the AstraZeneca vaccine reported more side effects after the first dose than people vaccinated with the other vaccines.
People who received the Moderna vaccine reported more side effects after the second and third doses compared to people who received the vaccine from Pfizer-BioNTech.
Several factors play a role in the reporting of menstrual changes
The second study showed that 30% of menstruating women reported changes in their menstrual cycle after being vaccinated against COVID-19.
The researchers examined which factors could potentially play a role in those changes and discovered that commonly known causes of menstrual changes, such as stress, age and smoking, had a correlation with the reported cycle changes after COVID-19 vaccination.
"We also found that women who had been concerned about the COVID-19 vaccine, who had had a severe COVID-19 infection or who reported experiencing several reactions to the vaccine were more likely to report menstrual changes after vaccination," says Christina Bisgaard Jensen, Ph.D. student at the Department of Public Health. She is the first author of the study, which has just been published in Human Reproduction.
"Changes in the menstrual cycle are not uncommon, and we cannot rule out that, for some people, the reported menstrual changes occurred randomly in temporal relation to the vaccination," says Christina Bisgaard Jensen, who further explains that the study cannot be used to identify a direct correlation between COVID1-9 vaccination and the reported menstrual changes.
"Further studies are needed to establish causal relationships and the clinical significance of self-reported menstrual changes," she says.
More information: K. Torp Hansen et al, Immediate adverse reactions following COVID-19 vaccination among 16–65-year-old Danish citizens, Vaccine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.06.069
C Bisgaard Jensen et al, Prevalence of and risk factors for self-reported menstrual changes following COVID-19 vaccination: a Danish cohort study, Human Reproduction (2023). DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dead144