This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Neural model shows evolution wired human brains to act like supercomputers
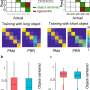
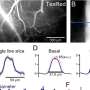
![Anisotropic univariate neural responses evoked by oriented gratings. a Schematic showing the experimental design; observers viewed rapidly presented oriented gratings (neural probe) while monitoring for target gratings with lower spatial frequency. Following the neural probe, participants indicated the number of target gratings detected using the mouse. b Difference in event related potentials for gratings within orientation bins ([0°, 30°, 60°, 90°, 120°, 150°] ±15°) from the grand average of responses, averaged over responses to all gratings. Signals averaged across parietal and occipital EEG sensors (blue dots on topographic map) and participants (n = 36). Orientation bin indicated in color; event-locked and subsequent gratings indicated by solid and dashed black rectangles, respectively, and cluster-corrected periods of significant difference between orientations indicated by horizontal black bars. c Time-averaged absolute signal amplitude for each grating orientation, binned to the nearest whole degree. The black line indicates the moving averages of data points. Credit: Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41027-w Evolution wired human brains to act like supercomputers](https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2023/evolution-wired-human.jpg)
Scientists have confirmed that human brains are naturally wired to perform advanced calculations, much like a high-powered computer, to make sense of the world through a process known as Bayesian inference.
In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Sydney, University of Queensland and University of Cambridge developed a specific mathematical model that closely matches how human brains work when it comes to reading vision. The model contained everything needed to carry out Bayesian inference.
Bayesian inference is a statistical method that combines prior knowledge with new evidence to make intelligent guesswork. For example, if you know what a dog looks like and you see a furry animal with four legs, you might use your prior knowledge to guess it's a dog.
This inherent capability enables people to interpret the environment with extraordinary precision and speed, unlike machines that can be bested by simple CAPTCHA security measures when prompted to identify fire hydrants in a panel of images.
The study's senior investigator Dr. Reuben Rideaux, from the University of Sydney's School of Psychology, said, "Despite the conceptual appeal and explanatory power of the Bayesian approach, how the brain calculates probabilities is largely mysterious."
"Our new study sheds light on this mystery. We discovered that the basic structure and connections within our brain's visual system are set up in a way that allows it to perform Bayesian inference on the sensory data it receives.
"What makes this finding significant is the confirmation that our brains have an inherent design that allows this advanced form of processing, enabling us to interpret our surroundings more effectively."
The study's findings not only confirm existing theories about the brain's use of Bayesian-like inference but open doors to new research and innovation, where the brain's natural ability for Bayesian inference can be harnessed for practical applications that benefit society.
"Our research, while primarily focused on visual perception, holds broader implications across the spectrum of neuroscience and psychology," Dr. Rideaux said.
"By understanding the fundamental mechanisms that the brain uses to process and interpret sensory data, we can pave the way for advancements in fields ranging from artificial intelligence, where mimicking such brain functions can revolutionize machine learning, to clinical neurology, potentially offering new strategies for therapeutic interventions in the future."
The research team, led by Dr. William Harrison, made the discovery by recording brain activity from volunteers while they passively viewed displays, engineered to elicit specific neural signals related to visual processing. They then devised mathematical models to compare a spectrum of competing hypotheses about how the human brain perceives vision.
More information: William J. Harrison et al, Neural tuning instantiates prior expectations in the human visual system, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41027-w