This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Pivotal role of TLR7 protein revealed in lung disease
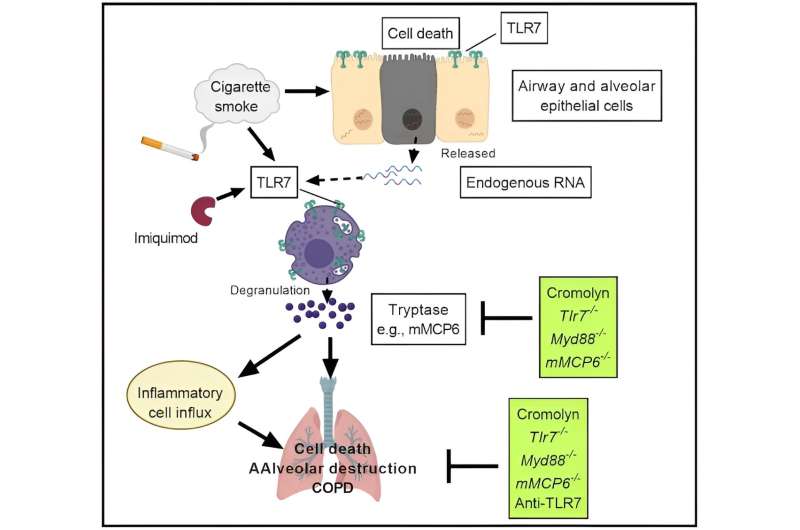
Researchers have revealed that the protein Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7), usually associated with antiviral defense in the body, surprisingly, exacerbates lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), also known as emphysema.
The discovery, led by the Centenary Institute and the University of Technology Sydney, could advance treatments for COPD, a lung condition that makes it difficult to breathe due to narrowed airways and damaged lung tissue. COPD is often caused by smoking or exposure to irritants.
Lead study researcher, Dr. Gang Liu at the Centenary UTS Center for Inflammation said that TLR7 is typically known for its vital role in supporting the immune system and its fight against certain types of viruses, including those responsible for influenza, measles and hepatitis C.
"Surprisingly, our research shows heightened TLR7 levels in individuals with COPD and also in experimental COPD models involving mice," Dr. Liu said. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
In further investigation, the researchers discovered that mice deficient in the TLR7 protein experience less severe lung issues when exposed to conditions resembling COPD. They also observed that imiquimod, a drug known to activate TLR7, exacerbates lung problems in mice with no pre-existing health issues.
"These preclinical findings shed light on TLR7's unexpected role in aggravating lung conditions," said Dr. Liu.
A significant finding highlighted in the study is that TLR7 increases the number and activity of mast cells, a type of immune cell known to be detrimental to COPD patients.
"Mast cells play a significant role in worsening COPD by initiating and perpetuating inflammation within the fragile lung tissues, making it harder for people to breathe. We found that higher TLR7 levels increases mast cell activity, escalating lung problems," said Dr. Liu.
Professor Phil Hansbro, senior study researcher and Director of the Centenary UTS Center for Inflammation said that they had unveiled a previously unknown dimension of TLR7 when it came to COPD.
"This study shows that TLR7, our body's defense system against certain viruses, unexpectedly worsens lung problems such as COPD by working with mast cells," said Professor Hansbro.
"Blocking TLR7 with targeted drugs could be a promising new therapeutic approach for COPD, a challenging lung condition which currently has no cure," he said.
More information: Gang Liu et al, TLR7 promotes smoke-induced experimental lung damage through the activity of mast cell tryptase, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42913-z