This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study provides clinician guidance on follow-up for ovarian cysts
About 15 to 20% of women will develop an ovarian cyst during their lifetime. The fluid-filled or solid sacs in the ovaries are usually non-cancerous and go away independently—studies show that about 85% resolve within five years.
Recent University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center research reveals patient characteristics associated with cysts that resolve independently and suggests that the time it takes for a cyst to resolve can vary depending on several variables.
The findings, published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, provide valuable guidance for doctors regarding how long and how often to monitor ovarian cysts.
"The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists currently recommends continued monitoring for cysts smaller than 10 centimeters, but there is no established duration for follow-up," said Ed Pavlik, Ph.D., lead author of the study and director of the UK Markey Cancer Center Ovarian Cancer Screening Program. "Our data provide guidelines so that clinicians can consider individual patient factors when determining the appropriate follow-up duration for ovarian cysts."
The research team examined data from over 2,600 participants in the UK Markey Cancer Center Ovarian Cancer Screening Program who had new ovarian cysts. They looked at whether the cysts resolved or persisted and how long it took for them to resolve. Researchers examined cyst type as well as patient characteristics, including age, menopausal status, BMI, and family history of ovarian cancer.
In the group, about 63% of cysts went away on their own within a year, and 37% persisted. Younger women and premenopausal women were more likely to have their cysts resolved. While older women were less likely to have cysts resolve, cysts among those over 70 years old resolved more quickly. Individuals using hormone therapy were more likely to have cysts that persisted. There was no difference in time to cyst resolution based on BMI or family history of ovarian cancer.
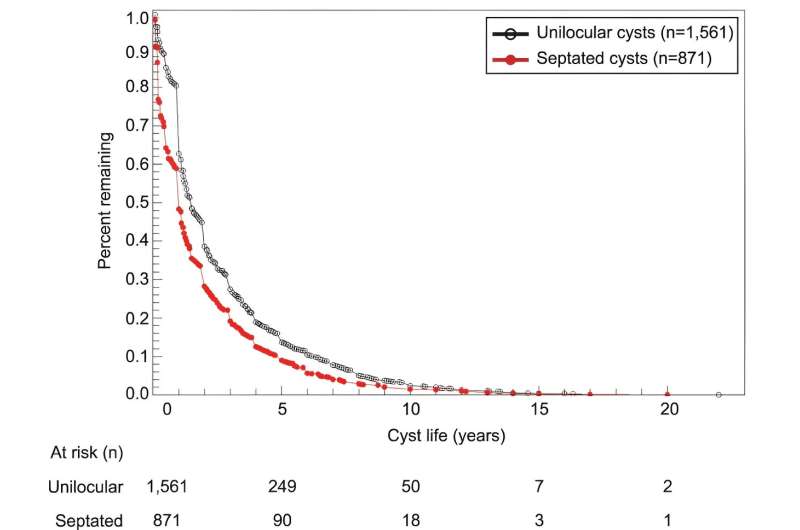
The size and type of cyst were also found to play a significant role in resolution time. Smaller cysts and cysts with a simple structure (unilocular) tended to disappear faster than larger cysts with septations.
Based on the findings, the report recommends guidelines for continued surveillance for both unilocular and septated cysts, depending on their size.
Since Markey's Ovarian Cancer Screening Program launched in 1987, over 51,000 participants have received over 370,000 free screenings—more than 1,200 per month—using transvaginal ultrasonography (TVS). TVS detects early-stage ovarian cancers, and the program results indicate that the screening reduces ovarian cancer deaths in the group screened.
More information: Anne Lasher et al, Variables Associated With Resolution and Persistence of Ovarian Cysts, Obstetrics & Gynecology (2023). DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000005411