This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Steroid drugs used for HRT can combat E. coli and MRSA
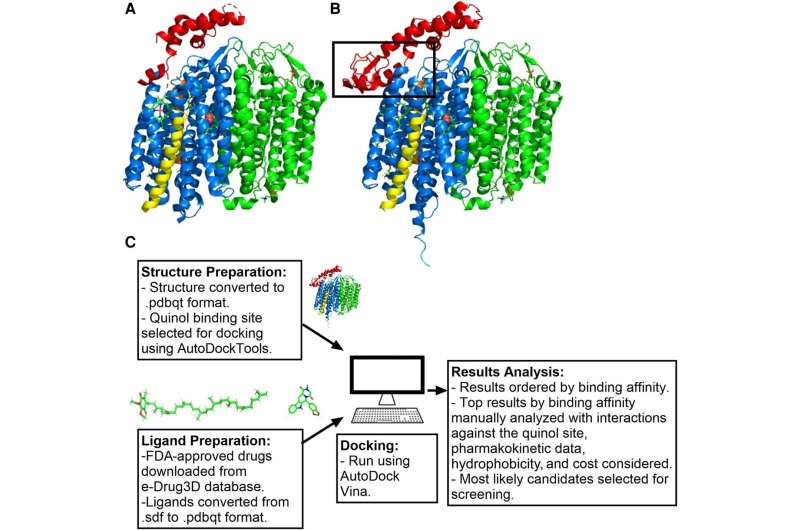
The emergence of drug-resistant bacteria is a global threat to human health, and the development of new antibiotics from scratch is an extremely expensive and time-consuming process. To address this urgent issue, researchers from the University of Kent's School of Biosciences have combined computational and microbiology laboratory approaches to identify existing drugs that can be repurposed to combat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
This research, which has been published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases, revealed that a class of steroid drugs currently used in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can also stop the growth of antibiotic-resistant E. coli and effectively kill MRSA. These drugs are particularly good at binding to a protein complex, cytochrome bd, which is important for the growth and survival of a range of disease-causing bacterial species. It is expected that steroids may provide an alternative to conventional antibiotics, which are becoming increasingly ineffective.
Dr. Mark Shepherd, Reader in Microbial Biochemistry at Kent and the corresponding author on the paper, said, "These exciting developments will help to advance research into new antimicrobials, and we are enthusiastic about using our powerful experimental approach to discover drugs that can target other bacterial proteins and combat a wide range of antibiotic-resistant infections."
The article "Steroid Drugs Inhibit Bacterial Respiratory Oxidases and Are Lethal Toward Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" is published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
More information: Samantha A Henry et al, Steroid Drugs Inhibit Bacterial Respiratory Oxidases and Are Lethal Toward Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, The Journal of Infectious Diseases (2023). DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad540