This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
Anxiety, depression associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease

Anxiety and depression are associated with an increased incidence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), according to a study published online March 19 in Scientific Reports.
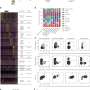
Qian Li, from The Third People's Hospital of Chengdu in China, and colleagues gathered 24-hour pH monitoring data and baseline patient information for a cohort of 518 individuals with GERD. In addition, their psychological well-being was assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.
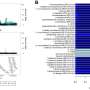
The researchers identified statistically significant variation in anxiety levels based on gender and significant disparity in depression based on age and literacy levels. In the patient cohort, there was a significant positive correlation observed between severity of anxiety and depression and the 24-hour pH monitoring results. A higher anxiety level was associated with a higher level of GERD in a logistic regression modeling analysis; the incidence of GERD was increased in the presence of mild anxiety (odds ratio, 2.64). A causal relationship was seen for the moderately severe anxiety group with increased GERD incidence (odds ratio, 6.84). A higher incidence of GERD was seen in association with moderate-to-severe depression (odds ratio, 2.32). GERD prevalence was increased among men versus women (odds ratio, 2.29). In addition, increased body mass index was positively associated with GERD susceptibility (odds ratio, 1.07).
"There is a certain correlation between GERD and anxiety and depression, which provides theoretical references for individuals and clinical workers to focus on patients' psychological emotions when treating GERD," the authors write.
More information: Qian Li et al, Analyzing the correlation between gastroesophageal reflux disease and anxiety and depression based on ordered logistic regression, Scientific Reports (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57101-2
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.