This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Newly discovered mechanism helps tumor cells evade the immune system early on
Tumors actively prevent the formation of immune responses by cytotoxic T cells, which are essential in combating cancer. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU) Hospital have now uncovered for the first time how this exactly happens.
The study, published in the journal Nature, provides rationales for new cancer immunotherapies and could make existing treatments more effective. A second paper in Nature confirms the findings.
In cancer, tumors often impair the body's immune response. For example, they can prevent immune cells from perceiving cancer cells as a threat or render them inactive. Immunotherapies aim to overcome these mechanisms and stimulate the immune system, in particular the T cells. However, such therapies do not work for a large number of cancer patients. Researchers around the world are looking for the causes and new counter-strategies.
Messenger substance stops effector development of T cells in tumors
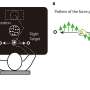
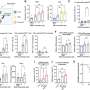
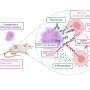
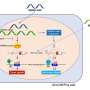
A team led by Dr. Jan Böttcher, research group leader at the Institute of Molecular Immunology at TUM, and Prof. Sebastian Kobold, Deputy Director of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology at LMU Klinikum München, has now discovered that tumors use a messenger substance to influence immune cells in an early phase of the immune response. Many cancer cells show increased secretion of the messenger substance prostaglandin E2. The researchers were able to show that prostaglandin E2 binds to EP2 and EP4, two receptors on the surface of certain immune cells.
These stem-like T cells migrate from other areas of the body into the tumor. If the immune response is successful, they multiply in the tumor and develop into cytotoxic T cells that attack the cancer. "This whole process is strongly limited when tumors secrete prostaglandin E2 and this factor binds to EP2 and EP4 receptors," says Böttcher. "The T cell response collapses and the tumor can progress." If the researchers prevented the interaction of messenger substance and receptor in tumor models, the immune system was able to fight tumors effectively.
"We have discovered a mechanism that influences the body's immune response in a crucial phase," says Böttcher. "Many tumors prevent the stem-like T cells from generating cytotoxic T cells in the tumor that could attack the cancer."
Current immunotherapies aim to prevent the cancer from switching off immune responses at a later phase. Checkpoint inhibitor therapies, for example, aim to release the blockade of fully differentiated cytotoxic T cells and "switch them back on." Before the dreaded T cell exhaustion sets in, which other researchers are trying to prevent, differentiated T cells must also be present.
"Current treatment approaches would probably be more effective if the effects of prostaglandin E2 on stem-like T cells is blocked to enable their unhindered differentiation within tumor tissue," says Kobold.
This similarly applies to recent approaches that rely on the protein IL-2 to stimulate T cells. The current study shows that as soon as the prostaglandin E2 binds to the two receptors, T cells can no longer respond to IL-2. "We suspect that even the body's own IL-2 signals may be sufficient to enable T cells to successfully fight cancer once the effects of prostaglandin E2 have been stopped," says Kobold.
A second research publication in Nature investigates the effects of prostaglandin E2 on the immune system. For this study, the authors, researchers from the University Hospital of Lausanne, collaborated with the Munich team. In their laboratory, they among other things examined T cells from human tumor tissue. When they blocked the release of prostaglandin E2 in cancer tissue, the T cells showed better expansion and were thus able to fight human cancer cells more effectively.
"We now have a concrete starting point for significantly improving immunotherapies," says Böttcher. "Researchers around the world must now develop strategies to overcome the tumors' defense. We need to stop the effects of prostaglandin E2—either by preventing tumors from producing the molecule or by making immune cells resistant to it."
More information: S.B. Lacher, Prostaglandin E2 curtails interleukin-2-dependent effector expansion from tumour infiltrating stem-like CD8+ T cells to promote cancer immune escape, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07254-x , www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07254-x
M. Morotti, PGE2 inhibits TIL expansion by disrupting IL-2 signalling and metabolism, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07352-w , www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07352-w