This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Scientists find cancer-like features in atherosclerosis, spurring opportunity for new treatment approaches
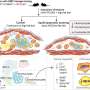
Researchers have discovered that the smooth muscle cells that line the arteries of people with atherosclerosis can change into new cell types and develop traits similar to cancer that worsen the disease. The study has been published in Circulation.
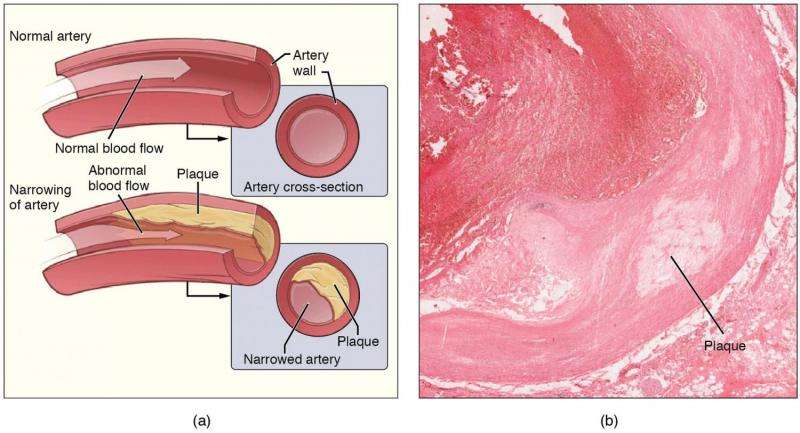
Atherosclerosis is characterized by a narrowing of arterial walls and can increase risk of coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders. The findings, supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), could pave the way for the use of anti-cancer drugs to counteract the tumor-like mechanisms driving the buildup of plaque in the arteries, the major cause of cardiovascular disease.
"This discovery opens up a whole new dimension for our understanding about therapeutic strategies for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis," said Ahmed Hasan, M.D., Ph.D., program director in the Division of Cardiovascular Sciences at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of NIH.
"Previous research has suggested that atherosclerosis and cancer may share some similarities, but this association has not been fully described until now."
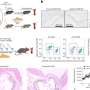
Using a combination of molecular techniques in mouse models and tissue samples taken from patients with atherosclerosis, the researchers characterized the molecular mechanisms that drive the smooth muscle cells to transition into cancer-like cell types.
The researchers found increased rates of DNA damage and genomic instability—two hallmarks of cancer—in the converted smooth muscle cells of atherosclerotic plaque when compared to healthy tissue. Genomic instability is the increased tendency for DNA mutations and other genetic changes to occur during cell division.
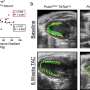
Probing further, they also found that cancer-associated genes became more active as the smooth muscle cells were being reprogrammed into the cells that made up the plaque. Using a mouse model expressing a known cancer mutation accelerated the reprogramming and worsened atherosclerosis. Finally, treating atherosclerotic mice with the anti-cancer drug niraparib, which targets DNA damage, showed potential for preventing and treating atherosclerosis.
"In fact, we saw that niraparib actually shrinks the atherosclerotic plaques in mice," said Huize Pan, Ph.D., assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and first author of the study.
Muredach Reilly, M.D., professor of Medicine at Columbia University, New York City, and senior author on the study, explained that understanding the molecular mechanisms that are driving the transition of smooth muscle cells can provide opportunities to disrupt tumor-like pathways and change how the cell behaves, in turn preventing or slowing progression of atherosclerosis.
More information: Pan H, Ho SE, Xue C, et al. Atherosclerosis is a smooth muscle cell-driven tumor-like disease Circulation (2024). DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.067587