This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Semaglutide significantly reduces risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes, study reveals
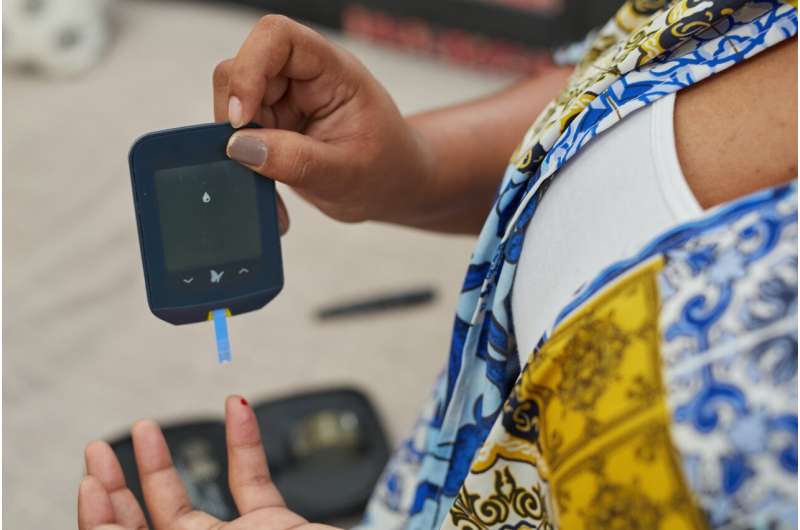

A pioneering study has demonstrated that semaglutide significantly reduces the risk of major kidney disease events, cardiovascular outcomes, and all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. The landmark trial, presented at the 61st ERA Congress, will pave the way for new treatment strategies and offer hope to millions of patients globally. The study is also published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The FLOW (Evaluate Renal Function with Semaglutide Once Weekly) study is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled international trial comprising 3,533 patients, with a median follow-up period of 3.4 years.
The trial was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of semaglutide, a once-weekly subcutaneous glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, in preventing major kidney outcomes, specifically kidney failure, substantial loss of kidney function, and death from kidney or cardiovascular causes, in individuals with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Patients either received semaglutide 1.0 mg once weekly or placebo.
Participants who received semaglutide had a 24% risk reduction for the composite primary endpoint, including kidney outcomes and death due to cardiovascular and kidney causes, compared to those who received placebo. This reduction risk was consistent across both kidney-specific and cardiovascular death outcomes.
Secondary endpoints also showed significant improvements with semaglutide. Specifically, the total eGFR slope was 1.16 ml/min/1.73 m2/year slower, the risk of major cardiovascular events was decreased by 18%, and the risk of all-cause mortality was reduced by 20%.
This evidence of efficacy, combined with fewer serious adverse events in the semaglutide group, offers hope to millions of patients globally who face the daunting prospect of chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes, and their related complications.
Professor Vlado Perkovic, who presented the results for the first time today at the 61st ERA Congress, emphasized the importance of these results, "The use of semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease can lower the risk of major kidney outcomes and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, cardiovascular death and all-cause death.
"These benefits signify a profound clinical impact saving kidneys, hearts and lives, for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Additionally, the reassuring safety findings further support the strong potential value of semaglutide in this population."
Chronic kidney disease affects over 800 million people worldwide and is particularly prevalent among individuals with type 2 diabetes. Chronic kidney disease poses a significant risk of kidney failure, cardiovascular events and death, highlighting the critical need for research into its prevention and treatment.
While current therapies have demonstrated kidney protection and reduced cardiovascular risks, many individuals continue to experience declining kidney function and adverse outcomes. This has sparked a growing interest in exploring new treatments, including GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Professor Vlado Perkovic further states, "These findings offer great promise in reshaping treatment strategies for individuals at high risk of diabetes-related complications, offering a new avenue for kidney and cardiovascular protection."
The FLOW trial was overseen by an academic-led Steering Committee, in partnership with the study sponsor, Novo Nordisk, which also managed trial operations.
More information: Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes, Perkovic V. et al. (2024). Presented at the ERA Congress 2024.
Vlado Perkovic et al, Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, New England Journal of Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2403347 , www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2403347