This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Study shows pregnant women admitted to intensive care in Scotland are 12 times more likely to experience a stillbirth
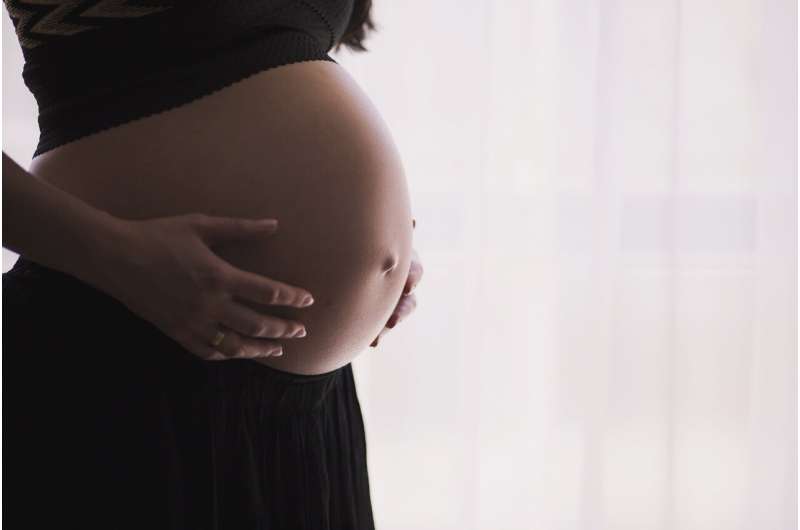

Women who require intensive care when pregnant are more likely to die compared with women who are not admitted—an excess risk that persists for up to a year after discharge from hospital, researchers also found.
Experts say the findings demonstrate the need for better tailored care for critically ill patients during and after a pregnancy.
Maternal death in the UK is known to occur in 12 in every 100,000 women, and is more common in women from ethnic minorities and those living in socially deprived areas. For each maternal death, a further 70 to 90 women develop severe illness.
The figures emerge at a time when risk factors for severe maternal illness are increasingly prevalent, such as more women with long-term health conditions becoming pregnant and increasing maternal age, underscoring a growing need to understand its long-term consequences.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh used national health care databases for more than 760,000 deliveries in Scottish hospitals between 2005 and 2018. This included all pregnancies resulting in a live birth, stillbirth or late miscarriage.
Some 1,449 women—almost one in 500—were admitted to intensive care. The most common reason for admission was postpartum hemorrhage—much heavier bleeding than normal after having a baby.
The study found that one in 16 women admitted to intensive care had a stillbirth, compared with one in 167 who are not admitted. Researchers also found that women admitted to intensive care had a 40 times higher risk of death than women who were not admitted. The most frequent cause of death was cardiovascular disease.
The study also showed that babies born to women admitted to intensive care were 13 times more likely to require a higher level of care after delivery.
Of the women who were discharged following intensive care, almost one-quarter were readmitted to hospital within a year compared with fewer than one in 10 of those who had never been admitted.
Researchers say that while many aspects of standard intensive care recovery services will be relevant to a maternity population, some elements of postpartum care may be better delivered by intensive care specialists in conjunction with maternity experts.
The study is published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine.
"Being admitted to intensive care can be a traumatic experience for many patients and their families. When this happens during or shortly after pregnancy, the impact on a woman, her baby and family can be devastating. Our study shows that women admitted to intensive care experience more health problems during the year after pregnancy.
"Maternity and critical care services need to develop a more joined up and proactive approach to better identify and support women who have ongoing care needs after becoming critically ill," says Nazir Lone, professor of critical care and epidemiology at the University of Edinburgh's Usher Institute and director of research for the Intensive Care Society.
More information: John A. Masterson et al, Measuring the impact of maternal critical care admission on short- and longer-term maternal and birth outcomes, Intensive Care Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.1007/s00134-024-07417-4