This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Guideline on management of central airway obstruction released

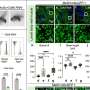
The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) recently released a new clinical guideline on central airway obstruction (CAO). Published in the journal CHEST, the guideline contains 12 evidence-based recommendations to guide the management of both malignant and nonmalignant CAO.
"Central airway obstruction is associated with a poor prognosis, and the management of CAO is highly variable dependent on the provider's expertise and local resources. By releasing this guideline, the panel hopes to standardize the definition of CAO and provide guidance for the management of patients to optimize care and improve outcomes," says Kamran Mahmood, MD, MPH, FCCP, lead author on the guideline.
"The guideline recommendations are developed using GRADE methodology and based on thorough evidence review and expert input. But the quality of overall evidence is very low, and the panel calls for well-designed studies and randomized controlled trials for the management of CAO."
CAO can be caused by a variety of malignant and nonmalignant disorders, and multiple specialists may be involved in the care, including pulmonologists, interventional pulmonologists, radiologists, anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, thoracic surgeons and otolaryngologists, etc. The panel recommends shared decision-making with the patients and a multidisciplinary approach to manage CAO.
Additional recommendations—all conditional with very low certainty of evidence—include:
- For patients with symptomatic malignant or nonmalignant CAO, we suggest therapeutic bronchoscopy as an adjunct to systemic medical therapy and/or local radiation.
- For patients with symptomatic malignant or nonmalignant CAO, we suggest the use of rigid bronchoscopy over flexible bronchoscopy for therapeutic interventions.
- For patients with symptomatic malignant or nonmalignant CAO, we suggest the use of general anesthesia/deep sedation over moderate sedation for therapeutic bronchoscopy.
- For patients with symptomatic malignant or nonmalignant CAO, we suggest stent placement if other therapeutic bronchoscopic and systemic treatments have failed and when feasible for the underlying disorder.
- For patients with nonmalignant CAO, we suggest either open surgical resection or therapeutic bronchoscopy.
- For patients with malignant CAO with endobronchial tumor, we suggest either surgical resection or therapeutic bronchoscopy for relief of initial obstruction.
The entire list of recommendations included in the new guideline can be accessed through the CHEST journal website.
More information: Kamran Mahmood et al, Management of Central Airway Obstruction. An American College of Chest Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline, CHEST (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2024.06.3804, journal.chestnet.org/article/S … (24)04614-2/fulltext