Shape-shifting disease proteins may explain variable appearance of neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are not all alike. Two individuals suffering from the same disease may experience very different age of onset, symptoms, severity, and constellation of impairments, as well as different rates of disease progression. Researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have shown one disease protein can morph into different strains and promote misfolding of other disease proteins commonly found in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and other related neurodegenerative diseases.
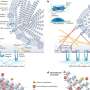
Virginia M.Y. Lee, PhD, MBA, professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine and director of the Center for Neurodegenerative Disease Research, with co-director, John Q. Trojanowski MD, PhD, postdoctoral fellow Jing L. Guo, PhD, and colleagues, discovered that alpha-synuclein, a protein that forms sticky clumps in the neurons of Parkinson's disease patients, can exist in at least two different structural shapes, or "strains," when it clumps into fibrils, despite having precisely the same chemical composition.
These two strains differ in their ability to promote fibril formation of normal alpha-synuclein, as well as the protein tau, which forms neurofibrillary tangles in individuals with Alzheimer's disease.
Importantly, these alpha-synuclein strains are not static; they somehow evolve, such that fibrils that initially cannot promote tau tangles acquire that ability after multiple rounds of "seeded" fibril formation in test tubes.
The findings appear in the July 3rd issue of Cell.
Morphed Misfolding Proteins Found In Overlapping Neurodegenerative Diseases
Tau and alpha-synuclein protein clumps are hallmarks of separate diseases – Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, respectively. Yet these two proteins are often found entangled in diseased brains of patients who may manifest symptoms of both disorders.
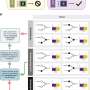
One possible explanation for this convergence of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease pathology in the same patient is a global disruption in protein folding. But, Guo and Lee showed that one strain of alpha-synuclein fibrils which cannot promote tau fibrillization actually evolved into another strain that could efficiently cause tau to fibrillize in cultured neurons, although both strains are identical at the amino acid sequence level. Guo and Lee called the starting conformation "Strain A," and the evolved conformation, "Strain B."
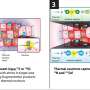
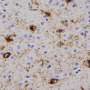
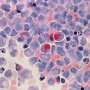
To figure out how A and B differ, Guo showed that the two strains folded into different shapes, as indicated by their differential reactivity to antibodies and sensitivity to protein-degrading enzymes. The two strains also differed in their ability to promote tau fibrillization and pathology in mouse brains, mimicking the results from cultured cells. When analyzing post-mortem brains of Parkinson's patients, the team found at least two distinct forms of pathological alpha-synuclein.
Lee and her team speculate that in humans, alpha-synuclein aggregates may shift their shapes as they pass from cell to cell (much like a cube of silly putty being re-shaped to form a sphere), possibly developing the ability to entangle other proteins such as tau along the way. That process, in turn, could theoretically yield distinct types of alpha-synuclein pathologies that are observed in different brain regions of Parkinson's disease patients.
While further research is needed to confirm and extend these findings, they have potentially significant implications for patients afflicted with Parkinson's and other neurodegenerative diseases. For example, Lee explains, they could account for some of the heterogeneity observed in Parkinson's disease. Different strains of pathological alpha-synuclein may promote formation of distinct types of alpha-synuclein aggregates that may or may not induce tau pathology in different brain regions and in different patients. That, in turn, could explain why some Parkinson's patients, for example, experience only motor impairments while others ultimately develop cognitive impairments.
The findings also have potential therapeutic implications, Lee says. By recognizing that pathological alpha-synuclein can exist in different forms that are linked with different impairments, researchers can now selectively target one or the other, or both, for instance with strain-selective antibodies.
"What we've found opens up new areas for developing therapies, and particularly immunotherapies, for Parkinson's and other neurodegenerative diseases," Lee says.
More information: Jing L. Guo et al. "Distinct α-Synuclein Strains Differentially Promote tau Inclusions in Neurons." Cell, July 3, 2013. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.057