Brain chemistry changes in children with autism offer clues to earlier detection and intervention
(Medical Xpress)—Between ages three and 10, children with autism spectrum disorder exhibit distinct brain chemical changes that differ from children with developmental delays and those with typical development, according to a new study led by University of Washington researchers.
The finding that early brain chemical alterations tend to normalize during the course of development in children with ASD gives new insight to efforts to improve early detection and intervention. The findings were reported July 31 in the Journal of the American Medical Assocation Psychiatry.
"In autism, we found a pattern of early chemical alterations at the cellular level that over time resolved – a pattern similar to what others have seen with people who have had a closed head injury and then got better," said Stephen R. Dager, a UW professor of radiology and adjunct professor of bioengineering and associate director of UW's Center on Human Development and Disability.
Neva Corrigan, a senior research fellow in radiology, was first author and Dager corresponding author of the study, titled "Atypical Developmental Patterns of Brain Chemistry in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder."
"The brain developmental abnormalities we observed in the children with autism are dynamic, not static. These early chemical alterations may hold clues as to specific processes at play in the disorder and, even more exciting, these changes may hold clues to reversing these processes," Dager said.
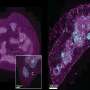
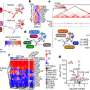
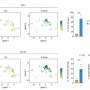
In the study, scientists compared brain chemistry among three groups of children: those with a diagnosis of ASD, those with a diagnosis of developmental delay, and those considered typically developing. The researchers used magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging, a type of MRI, to measure tissue-based chemicals in three age groups: 3-4 years, 6-7 years and 9-10 years.
One of the chemicals measured, N-acetylaspartate (NAA), is thought to play an important role in regulating synaptic connections and myelination. Its levels are decreased in people with conditions such as Alzheimer's, traumatic brain injury or stroke. Other chemicals examined in the study – choline, creatine, glutamine/glutamate and myo-inositol – help characterize brain tissue integrity and bioenergetic status.
A notable finding concerned changes in gray matter NAA concentration: In scans of the 3- to 4-year-olds, NAA concentrations were low in both the ASD and developmentally delayed groups. By 9 to 10 years, NAA levels in the children with ASD had caught up to the levels of the typically developing group, while low levels of NAA persisted in the developmentally delayed group.
"A substantial number of kids with early, severe autism symptoms make tremendous improvements. We're only measuring part of the iceberg, but this is a glimmer that we might be able to find a more specific period of vulnerability that we can measure and learn how to do something more proactively," said Annette Estes, a co-author of the study and director of the UW Autism Center. She is an associate professor of speech and hearing sciences.
Study co-author Dennis Shaw, a UW professor of radiology and director of MRI at Seattle Children's, observed that the findings "parallel some of the early brain structural differences we and others have found on MRI that also appear to normalize over time in children with autism. These chemical findings will help to better establish the timing and mechanisms underlying genetic abnormalities known to be involved in at least some cases of autism."
Dager and UW colleagues are currently using more advanced MRI methods to study infants at risk for ASD because of an older sibling with autism.
"We're looking prospectively at these children starting at 6 months to determine if we can detect very early alterations in brain cell signaling or related cellular disruption that may precede early, subtle clinical symptoms of ASD."
Despite the encouraging finding, science has yet to pinpoint the when, what and why of autism's inception, an event often likened to the flipping of a switch. Discovering the earliest period that a child's brain starts to develop a profile of ASD is crucial because, as the study acknowledged, "even a relatively brief period of abnormal signaling between glial cells and neurons during early development would likely have a lasting effect" on how a child's brain network develops.
This study also suggests that developmental delay and autism spectrum disorder are distinct disorders having different underlying brain mechanisms and treatment considerations, Dager said.
"Autism appears to have a different pathophysiology and different early biological course than idiopathic developmental disorder. There are differences in their underlying biological processes; this supports the notion that ASD is different from developmental delay and challenges the notion that the increasing prevalence of autism merely reflects a re-categorization of symptoms between autism and intellectual disabilities."
More information: archpsyc.jamanetwork.com/artic … px?articleid=1722813