Practices related to fluid volume that are important for dialysis patients' health
A new study highlights the importance of regular and careful assessment of dry or target weight and fluid balance in patients undergoing hemodialysis. The study appears in an upcoming issue of the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN).
In patients with kidney failure, dialysis helps remove excess fluid and waste products from the blood. This is important because too much fluid, or volume overload, can cause peripheral edema (swelling of legs) and breathlessness in the short-term, and hypertension (high blood pressure), left ventricular hypertrophy (enlargement of heart), and heart failure in the long-term. Removal of too much fluid, however, can cause cramps, abdominal pain, vomiting, and dizziness; and it can lead to intradialytic hypotension (acute drop in blood pressure during dialysis) which can cause damage to heart muscles and is associated with a higher risk of death.
Indranil Dasgupta, DM, FRCP (Heartlands Hospital, UK) and his colleagues compared the way patients' fluid volume was managed in different dialysis facilities and the effects this had on patient health.
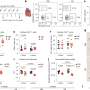
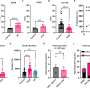
Data were analyzed from 10,250 patients and 270 facilities across 12 countries in the DOPPS (Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study). Medical directors of the dialysis centers were sent a questionnaire on fluid volume management of patients on hemodialysis, and the responses to 10 of the 29 questions, deemed most important by the researchers, were analyzed.
The researchers found that having a protocol that specifies how often to assess dry weight was associated with lower rates of all-cause and cardiovascular deaths. Routine postural (lying or sitting and standing) blood pressure measurement was associated with lower all-cause hospitalization and cardiovascular events. Routine use of lower dialysis temperature to prevent or limit intradialytic hypotension was associated with lower cardiovascular death.
The findings emphasize the importance of regular and careful clinical assessment of target weight and fluid balance in patients on hemodialysis.
"Dialysis units should consider how they can make sure every patient has their target weight assessed regularly, ideally before every treatment. This can be done by a doctor or nurse and should include careful measurement of blood pressure," said Dr. Dasgupta.
In an accompanying editorial, Andrew Davenport, MD, FRCP (Royal Free Hospital, UK) noted that the study raises numerous questions. "Answers to some of the subsidiary questions remain to be analyzed, and the responses analyzed so far open up further avenues that require greater exploration," he wrote.
More information: "Associations Between Hemodialysis Facility Practices to Manage Fluid Volume and Intradialytic Hypotension and Patient Outcomes," Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (2019). DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08240718