This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Diabetes researchers discover the potential of CIDEC protein to mitigate obesity-related cardiometabolic disease
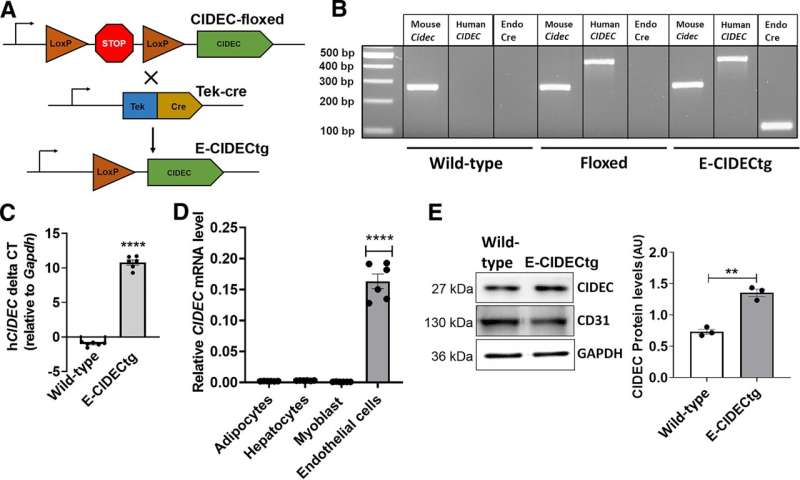
A team of researchers from Ohio University's Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine has recently discovered a novel role of human-CIDEC gene in improving metabolic dysfunction and cardiovascular health. Their study, "Endothelial-Specific Expression of CIDEC Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Vascular and Metabolic Dysfunction," published in Diabetes focuses on vascular function and its association with metabolic diseases like insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
"This is a very impactful study, and we have moved in the right direction to find a way to reduce cardiovascular diseases," said Vishwajeet Puri, Ph.D., professor of biomedical sciences and co-director of the Diabetes Institute. He was the principal investigator and senior author of the study. "When looking at diseases like diabetes and obesity, you cannot disassociate them from cardiovascular disease since they are all closely associated. Discoveries like this one allow us to not only manage the disease but work to cure it and help fight any related disorders."
According to Bijinu Balakrishnan, Ph.D., a scientist in Puri's lab who led the study, endothelial cells line the blood vessels and play a major role in maintaining vascular function, including blood pressure. He explains that endothelial dysfunction has a major role in the progression of insulin resistance, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and other metabolic diseases.
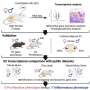
"We recently discovered that CIDEC, previously identified as fat-associated protein in adipocytes, is abundantly expressed in endothelial cells and regulates its function," Balakrishnan said. "The objective of the study was to find the mechanism of action of how human-CIDEC regulates the endothelial function and to determine its effect on whole-body physiology."
To conduct the study, the team of researchers generated humanized transgenic mice that expressed human CIDEC transgene, specifically in endothelial cells. Using mice as the model was instrumental in determining the cardiometabolic effects of the human-CIDEC gene and its role in protection against obesity-induced metabolic dysfunctions. To mimic the obese state in humans, the mice were fed a high-fat diet.
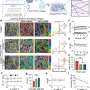
"These humanized transgenic mice showed protection against high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and displayed lower circulating lipid levels," Balakrishnan said.
"It's amazing to see that an endothelial-specific expression of a human transgene in mice could protect them from obesity-associated metabolic disorders," Puri added.
Their findings contribute to the understanding of the role of the vascular endothelium in regulating systemic metabolism and prompt recognition for potentially targeting the vasculature for the treatment of obesity-associated cardiometabolic disorders.
"Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide and have a significant negative influence on patient quality of life and disability," Balakrishnan said. "Endothelial dysfunction contributes significantly to the development and progression of cardiovascular pathophysiology and is considered an early predictor of cardiovascular events."
In addition to Puri and Balakrishnan, members of the research team from Ohio University's Heritage College also include Abhishek Gupta, Vishva M. Sharma, Mark Slayton, Rabia Basri, Kailey Gentner, Chloe Becker, Harrison Muturi, and Endowed Eminent Research Chair Sonia M. Najjar. The team also collaborated with researchers Shakun Karki and Noyan Gokce from Boston University School of Medicine, and Analia S. Loria from the University of Kentucky in Lexington.
"This study truly shows the power of teamwork and collaboration," Puri said. "It is thrilling to see the diversity of people contributing to advance science and medicine. We have researchers on this study with diverse ethnic backgrounds, with all sorts of experience levels ranging from established scientists to undergraduate students, and with all types of areas of expertise such as cardiologists, cell biologists, physiologists and more."
More information: Bijinu Balakrishnan et al, Endothelial-Specific Expression of CIDEC Improves High-Fat Diet–Induced Vascular and Metabolic Dysfunction, Diabetes (2023). DOI: 10.2337/db22-0294