This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Nerve cells in the brain can halt all movement in the body—even breathing
When a hunting dog picks up the scent of a deer, it sometimes freezes. On the spot. The same thing can happen to people who need to concentrate on a challenging task.
Now researchers have made a discovery that adds to our knowledge of what happens in the brain when we suddenly stop moving. Their study is published in Nature Neuroscience.
"We have found a group of nerve cells in the midbrain which, when stimulated, stop all movement. Not just walking; all forms of motor activity. They even make the mice stop breathing or breathe more slowly, and the heart rate slow down," explains Professor Ole Kiehn, who is co-author on the study.
"There are various ways to stop movement. What is so special about these nerve cells is that once activated they cause the the movement to be paused or freeze. Just like setting a film on pause. The actors movement suddenly stop on the spot," says Ole Kiehn.
When the researchers ended activating the nerve cells, the mice would start the movement exactly where it stopped. Just like when pressing "play" again.
"This 'pause-and-play pattern' is very unique; it is unlike anything we have seen before. It does not resemble other forms of movement or motor arrest we or other researchers have studied. There, the movement does not necessarily start where it stopped, but may start over with a new pattern," says Ph.D. Haizea Goñi-Erro, who is first author of the study.
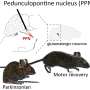
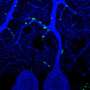
The nerve cells stimulated by the researchers are found in the midbrain in an area called the pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN), and they differ from other nerve cells there by expressing a specific molecular marker called Chx10. The PPN is common to all vertebrates including humans. So even though the study was performed in mice, the researchers expect the phenomenon to apply to humans too.
Not related to fear
Some might suggest that the nerve cells are activated by fear. Most people are familiar with the phenomenon of "freezing" caused by extreme fear. But that is not the case.
"We have compared this type of motor arrest to motor arrest or freezing caused by fear, and they are not identical. We are very sure that the movement arrest observe here is not related to fear. Instead, we believe it has something to do with attention or alertness, which is seen in certain situations," says Assistant Professor Roberto Leiras, who is co-author of the study.
The researchers believe it is an expression of a focused attention. However, they stress that the study has not revealed if this is indeed the case. It is something that requires more research to demonstrate.
May help understand Parkinson's symptoms
The new study may be able to help us understand some of the mechanisms of Parkinson's disease.
"Motor arrest or slow movement is one of the cardinal symptoms of Parkinson's disease. We speculate that these special nerve cells in PPN are over-activated in Parkinson's disease. That would inhibit movement. Therefore, the study, which primarily has focused on the fundamental mechanisms that control movement in the nervous system, may eventually help us to understand the cause of some of the motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease," Ole Kiehn concludes.
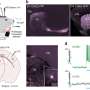
Among other things, the researchers used optogenetics to stimulate the nerve cells in the brainstem.
In short, optogenetics is a biological technique that involves genetically modifying specific brain cells to make them more sensitive to light. This means that the cells can be activated by a flash of light.
In the study, the researchers were able to stimulate the specific group of nerve cells in mice and thus determine the motor function of these cells.
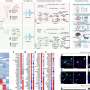
More information: Haizea Goñi-Erro et al, Pedunculopontine Chx10+ neurons control global motor arrest in mice, Nature Neuroscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01396-3