This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Training immune cells to remove 'trash' helps resolve lung inflammation
Inflammation is a standard part of our bodies' immune system response. But sometimes this response becomes hyperactivated in our lungs, causing inflammation to continue unchecked, which can be fatal. Many deaths from COVID-19 have been due to excessive inflammation, which results in acute lung injury.
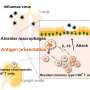
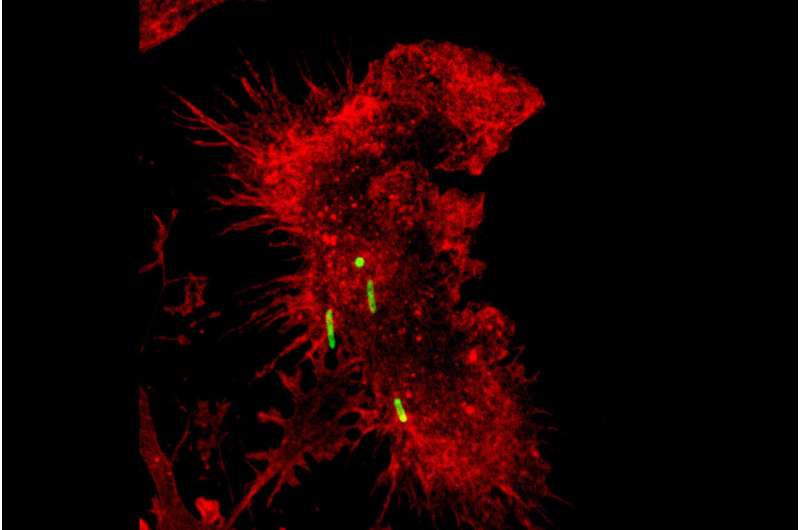
A group of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have investigated how lungs counterbalance inflammation. Their work points to cells in the lung that reduce inflammation by removing cellular debris, ingesting harmful bacteria and releasing anti-inflammatory proteins. What's more, these cells can be trained by an initial infection to do this job even better during a subsequent infection.
The scientists demonstrated that injecting these trained cells into mice helped keep them alive after an infection with pneumonia. These results suggest that such trained cells could become part of a cell therapy that prevents excessive inflammation. The research is published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
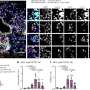
The researchers found that after an initial exposure to a bacterial toxin, lung immune cells called alveolar macrophages helped reduce the severity of inflammation brought on by a second exposure to the bacterial toxin one week later. The benefit of this "memory" or "training" was present even when the second exposure occurred a month later, explained senior author Dr. Jalees Rehman, Benjamin Goldberg Professor and head of the UIC Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics.
The cells appear to become particularly good at removing post-infection debris—such as cellular debris from immune cells that fought the infection or from one's damaged tissue—Rehman explained. "Clearing out this debris is important because its persistence can trigger the immune system to continue to react, thus increasing inflammation," Rehman said.
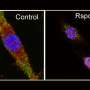
Because this debris isn't specific to one type of infection, these trained macrophages might help reduce the risk of acute lung injury from subsequent infections that arise from a different disease. The researchers found that the molecules involved in the removal of cell debris were higher in the trained alveolar macrophages.
Alveolar macrophages are unusual cells in that we are born with them and they stay in our lungs into adulthood. During infections, alveolar macrophages die but they can regenerate from surviving alveolar macrophages. They also pass along epigenetic information to their cellular progeny, which means new macrophages could retain a memory of previous infections, Rehman explained. All of this combines to make them very effective in helping to reduce acute lung injury.
Many other organs have macrophages, so future research could explore whether those cells could be trained by an initial infection as well or by directly increasing the levels of the molecules that help with debris removal, said Rehman, who is also a member of the University of Illinois Cancer Center.
More information: Sreeparna Chakraborty et al, Trained immunity of alveolar macrophages enhances injury resolution via KLF4-MERTK-mediated efferocytosis, Journal of Experimental Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1084/jem.20221388