This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Feedback loop promotes cancer cells' adaption to molecular stress
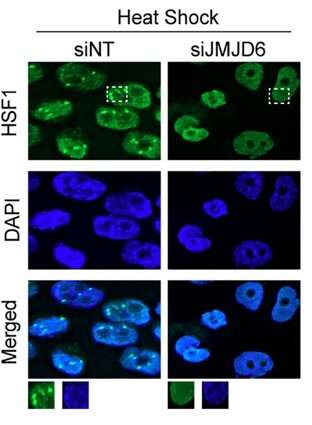
Investigators from the laboratory of Marc Mendillo, Ph.D., associate professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, have discovered new cellular regulators of a cancer cell transcription factor linked to cancer resilience and tumor progression, according to findings published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) is a transcription factor best known for inducing the cell's heat shock response, which involves increasing the amount of heat shock proteins that act as helper proteins that ensure proper protein folding and support cellular function.
Mendillo's laboratory had also previously discovered how HSF1 and its paralog, HSF2, drive a distinct gene expression program in cancer cells comprising not only heat shock protein genes, but also many other non-canonical genes that promote cancer cell resilience and tumor progression.
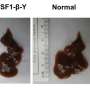
"That's why we think cancer cells are so difficult to kill. They have these remarkable abilities to disassociate from their primary site, survive the circulatory system, colonize a tissue where they're not supposed to be and survive radiation and chemotherapy," said Mendillo, a member of the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University.
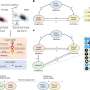
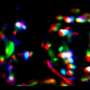
To identify additional modulators of HSF1 activity in cancer, Mendillo's team utilized a combination of genetic, biochemical and genomic techniques to study human embryonic kidney (HEK) cell lines that had been exposed to proteotoxic stress.
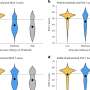
They discovered that HSF1 activity is mediated by a protein called the Jumonji domain-containing protein 6 (JMJD6), which regulates protein homeostasis through a positive feedback circuit: HSF1 binds to and promotes JMJD6 expression, which in turn regulates a key HSF1 target gene, HSP70, resulting in enhanced HSF1 activation.
"This is important in that it enables rapid switching of HSF1 activity in response to stress rather than producing and degrading HSF1, which is time and energy consuming," said Milad Alasady, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the Mendillo laboratory and lead author of the study.
"We immediately thought that was interesting, because a gene that HSF1 regulates in cancer that we thought had nothing to do with protein homeostasis instead feeds back to regulate HSF1 itself," Mendillo said.
"This suggests that a lot of these non-canonical targets do have some sort of role in enabling HSF1's function and cancer cell resilience in a way that's really connected with HSF1's role in protein homeostasis and stress response."
The investigators are now interested in identifying other noncanonical targets of HSF1 and how they contribute to HSF1 activity, which could inform the development of new targeted cancer therapies, Mendillo said.
"JMJD6 has an enzymatic activity, and it's thought to be an easier drug target, as compared to HSF1 which is a transcription factor, which are generally thought to be more challenging to target, although this is not impossible anymore," Mendillo said.
"So, we think that this may be a druggable regulator of a critical switch controlling HSF1, so we're interested in pursuing that direction because we think that will have relevance in cancer and perhaps other diseases."
More information: Milad J. Alasady et al, An HSF1–JMJD6–HSP feedback circuit promotes cell adaptation to proteotoxic stress, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2313370121