Last update:
Genetics
Largest-ever genetic study of epilepsy finds possible therapeutic targets
The largest and most diverse study to date of epilepsy's genetic factors has revealed new potential targets for treatment, both shared by and unique to different subtypes of epilepsy. The findings point to factors involved ...
13 hours ago
0
88
Immunology
Here's why B cells benefit from booster shots
Certain infectious diseases, such as COVID or the flu, evolve constantly, shapeshifting just enough to outmaneuver our immune systems and reinfect us repeatedly. But subsequent reinfections often don't lead to the most severe ...
13 hours ago
0
18
Medical research news
Brain scan study shows what happens in the brain when a person with schizophrenia hears voices
Auditory hallucinations are likely the result of abnormalities in two brain processes: a "broken" corollary discharge that fails to suppress self-generated sounds, and a "noisy" efference copy that makes the brain hear these ...
15 hours ago
0
30

How doxycycline for STI prevention affects the gut microbiome
Taking a dose of the oral antibiotic doxycycline after a high-risk sexual encounter has dramatically reduced the incidence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in places where the strategy is being tried.
14 hours ago
0
22

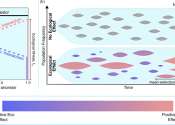
Small brains can accomplish big things, according to new theoretical research
Neuroscientists had a problem. For decades, researchers had a theory about how an animal's brain keeps track of where it is relative to its surroundings without outside cues—like how we know where we are, even with our ...
14 hours ago
0
67

Live-cell model system can decode genetic risk for psychiatric disorders
For many years, scientists have known that genetic variants, or differences in DNA code across people, play some role in neurological and psychiatric disorders. But the details were murky. Now, researchers at the UNC School ...
14 hours ago
0
40

New web portal empowers drug discovery, systems-level analysis of critical kinase-substrate interactions
Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have introduced KiNet, an interactive web portal designed to explore kinase-substrate interactions in human cellular systems. These interactions play a vital role ...
13 hours ago
0
0

New imaging technique accurately detects aggressive kidney cancer
A new study led by investigators from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has demonstrated a new, non-invasive imaging technique can accurately detect clear-cell renal cell carcinoma, the most common form ...
14 hours ago
0
21

Smartphone-assisted wayfinding task identifies people at risk for dementia
Researchers from DZNE and Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg have identified individuals with increased risk for dementia using mobility data, recorded during a smartphone-based wayfinding task on the university campus.
15 hours ago
0
2

Turning brain cells on using the power of light: Researchers refine noninvasive method of bioluminescent optogenetics
University of Rochester researchers have demonstrated a noninvasive method using BL-OG, or bioluminescent optogenetics, that harnesses light to activate neurons in the brain. The ability to regulate brain activation could ...
15 hours ago
0
20

Water fluoridation found to be less effective now than in past
The dental health benefits of adding fluoride to drinking water may be smaller now than before fluoride toothpaste was widely available, an updated Cochrane review has found.
9 hours ago
0
15

Scientists discover new mechanism controlling T-cells in inflammation
Northwestern Medicine scientists have discovered a new mechanism that controls a specialized group of T-cells, known as regulatory T-cells, and may serve as potential therapeutic targets to treat inflammatory disorders and ...
16 hours ago
0
22

Our brains divide the day into chapters: Psychology research offers details on how
The moment a person steps off the street and into a restaurant—to take just one example—the brain mentally starts a new "chapter" of the day, a change that causes a big shift in brain activity. Shifts like this happen ...
18 hours ago
0
51

Study finds toddlers get nearly half their calories from ultra-processed foods
Toddlers in the UK obtain nearly half (47%) of their calories from ultra-processed foods (UPFs), and this rises to 59% by the age of seven, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
9 hours ago
0
2

From kitchenware to toys, household items linked to toxic flame retardants
From toys to kitchenware to food takeout trays, researchers have discovered a toxic chemical banned for its link to cancer in many common household items. Exposure to the flame retardant can come with serious health risks.
16 hours ago
0
11

Researchers use AI to help people see more clearly
Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is on the rise, especially among children. Experts predict that by the year 2050, myopia will affect approximately 50% of the world's population. Researchers believe that an increase ...
17 hours ago
0
38

Microbiome-directed food speeds recovery in children with severe acute malnutrition, trial finds
A team of biologists, nutritionists and gut biome specialists has found via a trial run at several hospitals in Bangladesh that giving children suffering from severe malnutrition a microbiome-based food helps them recover ...

Stem cell transplants repair macular holes in primate study
Human stem cell transplants successfully repaired macular holes in a monkey model, researchers report October 3 in the journal Stem Cell Reports. After transplantation, the macular holes were closed by continuous filling ...
18 hours ago
0
34

New insights into diabetes-related vision problems to inform treatment and prevention
A study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences details the role of the protein Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) in diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness and visual impairment.
18 hours ago
0
42

Unlocking new regenerative pathways in iPS cell–derived epicardium for cardiac repair
Efforts to foster both intrinsic and extrinsic regenerative responses in heart failure have once again brought iPS cell technologies to the forefront, thanks to their flexibility in reconstructing tissues in vitro and enabling ...
17 hours ago
0
2