Synchronized brain waves in distant regions combine memories
Humans have the remarkable ability to integrate information from multiple memories and infer indirect relationships. How does our brain support this important function? Neuroscientists from the Donders Institute at Radboud University have now shown that rhythmic brain waves, called theta oscillations, engage and synchronize the brain regions that support the integration of memories. The results were published in the journal Current Biology on January 28.
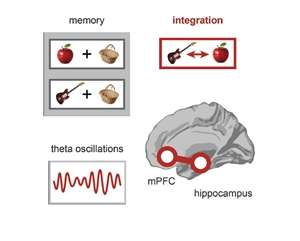
Activity in the brain is not constantly high or low, but rather organized in waves that come and go. For one type of wave, called theta, activity goes up and down a couple of times per second. "We know from previous work that the theta rhythm is important for memory, and also that temporal and frontal brain regions interact when you combine memories" says Christian Doeller, senior author of the study. "Here we bring these two observations together, by showing that theta oscillations are crucial for memory integration."
Signals from deep inside the brain
There was one problem: in healthy individuals, brain oscillations can only be measured from outside the brain. This complicates measurements of signals from structures deep inside the brain, like the hippocampus: a key brain region for memory. "We had to use advanced computational techniques to reconstruct oscillatory signals from the hippocampus" says lead researcher Alexander Backus. "Using these hippocampal signals, we found that the amount of theta oscillations increased whenever someone succeeds in linking two separate memories". In addition, the researchers saw that theta oscillations from hippocampus were synchronized with the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), a brain region involved in storing knowledge networks.
Communication through synchronization
According to Backus, distant brain regions are able to communicate by synchronizing their theta waves, enabling them to integrate previously stored memories. The findings are important for certain diseases linked to memory integration. For instance in post-traumatic stress disorder, memories from a past traumatic event are mistakenly linked to everyday life situations. The results of this study might bring us closer to the neurobiological mechanisms underlying such conditions.
According to Doeller, the key observations of the study also have a big impact on our understanding of higher cognitive functions: "The ability to combine information from different memories is what allows us to make decisions based on past experience. Ultimately, this is how we acquire knowledge about our world."
More information: Alexander R. Backus et al. Hippocampal-Prefrontal Theta Oscillations Support Memory Integration, Current Biology (2016). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.048