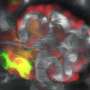
Fluctuation in the concentration of calcium ions contributes to brain shape
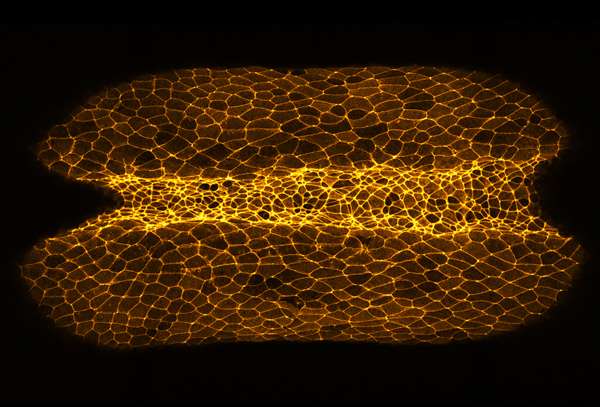
The first step in shaping the brain is that the neural plate, a sheet-like cell layer, curves to form the neural tube. Assistant Professor Makoto Suzuki of the National Institute for Basic Biology, Professor Naoto Ueno, and their colleagues have shown that during the process of neural tube formation a transient increase in the concentration of calcium ions in cells causes these morphological changes and is essential for neural tube formation.
This result was published in the journal Development March 28, 2017 and an image from this research was selected for the cover.
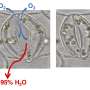
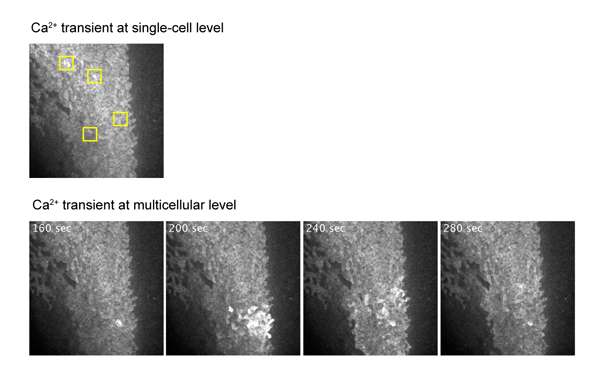
In this study, the researchers observed the cell population during neural tube formation in the embryos of African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) using the fluorescent protein GECO, the brightness of which varies depending on the intracellular calcium ion concentration. As a result, they found that the pattern of the fluctuation in intracellular calcium ion concentration in the cell population is complex. Local and transient rises in intracellular calcium ion concentrations have been found to cause cell deformation and contribute to the formation of the neural tube.
Suzuki said, "According to these results, in the elevated pattern of calcium ions, we found that there is a pattern randomly occurring in single cells, and a pattern that occurs synchronously in many neighboring cells. It was found that the morphological changes necessary for normal neural tube formation occurred by combining these different patterns."
More information: Makoto Suzuki et al, Distinct intracellular Cadynamics regulate apical constriction and differentially contribute to neural tube closure, Development (2017). DOI: 10.1242/dev.141952