New data changes the way scientists explain how cancer tumors develop
A collaborative research team has uncovered new information that more accurately explains how cancerous tumors grow within the body. This study is currently available in Nature Genetics.
Researchers led by scientists at The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston and Baylor College of Medicine found that a losing a section of messenger RNA that was previously thought to transform normal cells into cancerous ones actually acts by blocking a body's ability suppress the formation of tumors. The finding could completely alter the way that medical science approaches the formation of tumors.
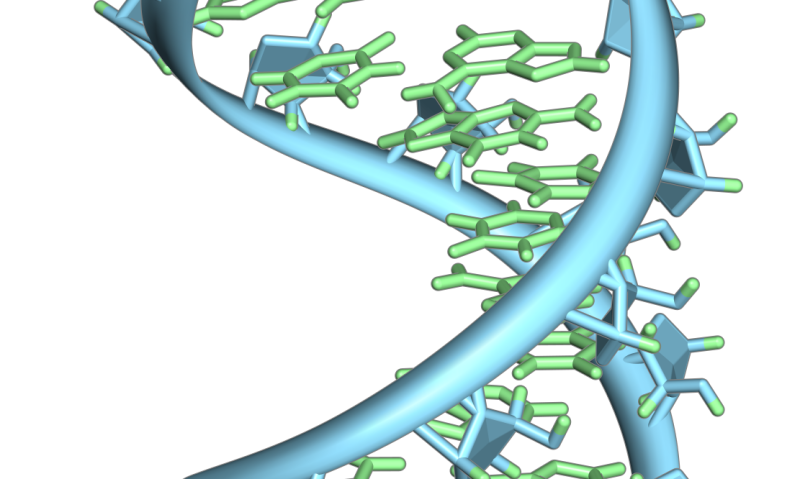
In molecules throughout the body, the three-prime untranslated region, or 3'UTR, is a section of messenger RNA that can alter gene expression. It's known that shortening this RNA section promotes cancerous tumor growth.
"Researchers have historically thought that this was because 3'UTR shortening induces the expression of proto-oncogenes, normal genes that when altered by mutation or expressed too high, become oncogenes that can transform a normal cell into a cancer cell," said Eric Wagner, UTMB associate professor in the department of biochemistry and molecular biology. "However, using a combination of computational approaches and cancer cell models, we found that 3'UTR shortening in tumors actually causes tumor-suppressing genes to be turned off."
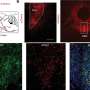
In the study, the researchers used "Big data" analyses to reconstruct the RNA thought to form global regulatory networks within breast tumor cells and their matched normal tissues. This approach identified the fact that 3'UTRs are vital in regulating these global regulatory networks. Using this new information, they then disrupted these networks within breast cancer cells to test the effects on tumor growth.
More information: Hyun Jung Park et al. 3′ UTR shortening represses tumor-suppressor genes in trans by disrupting ceRNA crosstalk, Nature Genetics (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0118-8