HIV latency differs across tissues in the body
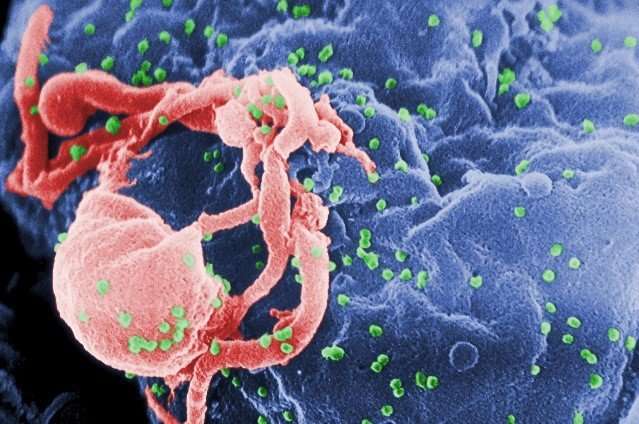
Mechanisms that govern HIV transcription and latency differ in the gut and blood, according to a study published November 15 in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens by Steven Yukl of San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center and the University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues. According to the authors, the findings could inform new therapies aimed at curing HIV.
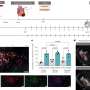
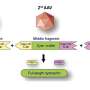
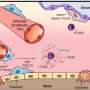
Available antiretroviral drugs significantly prolong life expectancy in people living with HIV. However, the virus can escape host defenses and drug treatment by establishing a reversibly silent infection in immune cells that produce a protein called CD4 (i.e., CD4+ T cells). This latent infection, which is characterized by inactivated HIV transcription, represents the major barrier to a cure. While much of the research to date has highlighted the importance of CD4+ T cells in the blood as reservoirs for latent HIV, it is becoming increasingly apparent that the gut may play an integral role as a major tissue reservoir for the virus. To compare the mechanisms that inhibit HIV transcription in the gut and blood, Yukl and his colleagues quantified HIV transcripts in cells from the blood and rectum of HIV-infected individuals effectively treated with antiretroviral drugs.
The researchers found that different mechanisms block HIV transcription and underlie HIV latency in CD4+ T cells in the blood and gut. Moreover, the findings suggest that the rectum may be enriched for latently infected cells, or cells in a deeper state of latency. These differences in the blocks to HIV transcription are important to consider in designing therapies that aim to disrupt HIV latency in all tissue compartments. In particular, infected cells in the rectum may be less susceptible to agents designed to reverse latency or may require different types of therapies.
More information: Telwatte S, Lee S, Somsouk M, Hatano H, Baker C, Kaiser P, et al. (2018) Gut and blood differ in constitutive blocks to HIV transcription, suggesting tissue-specific differences in the mechanisms that govern HIV latency. PLoS Pathog 14(11): e1007357. doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007357