A potential Diamond-Blackfan anemia treatment swims into view
Zebrafish, besides being popular in aquariums, make good stand-ins for studying human diseases. They share about 70 percent of their genes with humans, and can be studied at a mass scale, enabling scientists to test hundreds, even thousands of drugs at a time simply by adding the drug to their water.
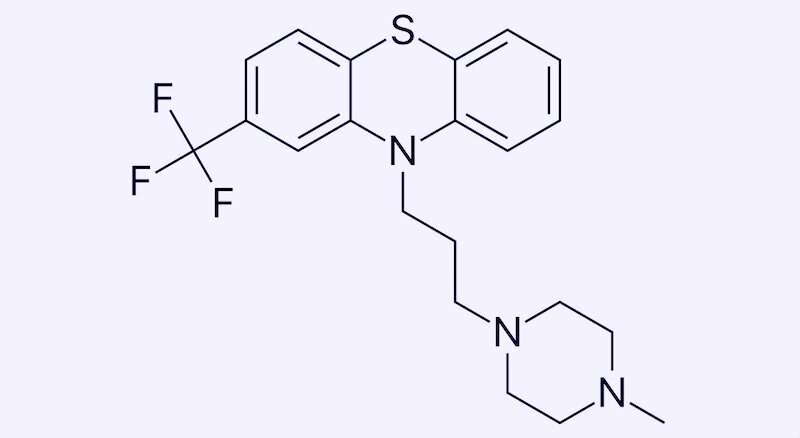
One such test came up with a new potential treatment for a rare blood disorder, Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA): a drug called trifluoperazine, normally used to treat psychotic disorders. It's now in a clinical trial for DBA in adults, and Leonard Zon, MD, hematology/oncology researcher and director of the Stem Cell Research program at Boston Children's Hospital, counts it as the fourth drug his team has identified in zebrafish to reach patients.
"We're excited to participate in this trial," says Akiko Shimamura, MD, Ph.D., director of the Bone Marrow Failure and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Program at the Dana-Farber/Boston Children's Cancer and Blood Disorders Center. "DBA was first described in our hematology division, and we are committed to translating basic science discoveries to help our patients. The identification of new therapies that are more effective and less toxic would be a major advance for these patients. "
Missing red blood cells
As Louis K. Diamond, MD, and Kenneth Blackfan, MD, of Boston Children's described in 1938, children with DBA are unable to produce mature, functioning red blood cells. Their bone marrow begins the process, creating progenitor cells called pro-erythroblasts. But the cells can't differentiate further and instead die off. Even today, the only treatment is corticosteroids, which fail in around 20 percent of patients or cause prohibitive side effects. Many patients must rely on lifelong blood transfusions to get the red cells they need.
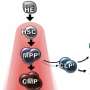
Over the past two decades, in part through work at Boston Children's, DBA's genetic causes have come into focus, revealing that most mutations are in genes for various proteins in ribosomes, cell organelles that themselves build proteins. The mutations leave progenitor cells with too few functioning ribosomes to make red cells.
Helping red blood cell progenitors stay alive
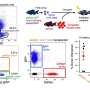
Zon and his colleagues decided to delve further with zebrafish. They created a line of fish deficient in one of the ribosomal proteins, rps29, discovered by the lab to be mutated in DBA. Looking at the zebrafish embryos, the team could see that they had very few red blood cells, similar to people with DBA.
In experiments, the team found that the p53 pathway, known to regulate the cell cycle and known to be involved in DBA, becomes more active when rps29 is deficient, helping trigger the death of red blood cell progenitors. When Zon's team deliberately mutated p53 in their rps29-deficient zebrafish, the progenitor cells survived and began making red blood cells.
"As in human patients, blood development in our fish mutant was blocked at the pro-erythroblast stage," explains Zon. "But if we took out p53 and blocked cell death, red blood cells would appear. We then asked, can we find a drug that would alter p53 action and rescue the disease?"
Zon and colleagues put their rps29-deficient zebrafish into their high-throughput drug screening system, loading the tiny embryos onto plates and exposing them to libraries of known compounds, including many drugs already approved by the FDA. They found that red blood cell production revived in fish exposed to drugs known as calmodulin inhibitors, including trifluoperazine (TFP). TFP also restored red blood cell development in a mouse model of DBA, also involving mutation of rps29.
From zebrafish to mice to humans
In separate experiments, Zon and colleagues mutated rps19, the most common gene mutated in DBA, in human red blood cell progenitors. The mutated cells were unable to differentiate into red blood cells, but they could do so when TFP was added.
The Phase 2 clinical trial of TFP, led by Adrianna Vlachos, MD, of the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health (Long Island, NY), will enroll six patients at the time and give them escalating doses of TFP.
Zon believes that if TFP does well in the trial, it could also benefit patients with DBA caused by other ribosomal protein mutations, and even some patients with other anemias. His lab is working on modifications of the drug to minimize its known side effects.
"All forms of DBA have a block to red cell differentiation, so this drug could potentially rescue them all, as well as other anemias that have this cell death problem," he says.
Probing DBA with iPS cells
In related work, the Zon lab partnered with the Boston Children's lab of George Daley, MD, Ph.D., to model RPS19 mutations in blood progenitor cells made from two patients with DBA, using induced pluripotent stem cell technology. They loaded the cells into a high-throughput drug screening system and identified another compound, SMER28, that boosted numbers of erythroid progenitor cells and, in turn, red blood cells, when added to the cultures. (This drug hasn't yet progressed to the clinic.)
As for zebrafish, they've also led to clinical trials of new drugs for adenoid cystic carcinoma and melanoma, and a drug enhancing cord blood transplants for cancer and blood disorders.