A potentially novel approach to improving the efficacy of natural killer cell therapies
Natural killer (NK) cells have lately become a hot focus of efforts to develop new immunotherapies. Researchers led by Ludwig Harvard's Tony Letai, whose team collaborated closely with the Ludwig Harvard Kai Wucherpfennig lab in this study, reported in an April issue of Cell a potentially novel approach to improving the efficacy of NK cell therapies.
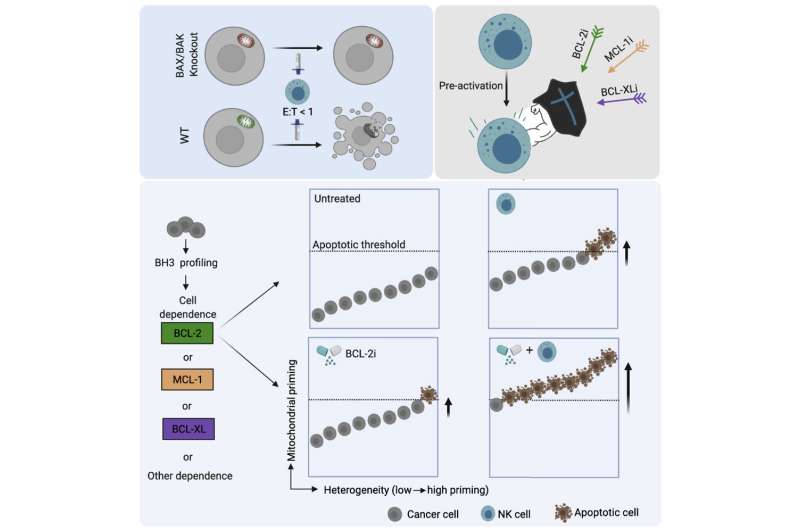
The new strategy described by Letai and his team builds on their discovery that NK cell-induced apoptosis of cancer cells occurs through a signaling pathway that involves the mitochondria. This mechanism—"mtApoptosis"— depends on the balance of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins in the mitochondrion. Whether a cell destroys itself depends on which way that balance is tipped. The researchers showed that targeting by NK cells tips the balance in favor of pro-apoptotic proteins and so primes cancer cells for mtApoptosis.
Combining NK cells with a class of drugs—BH3 mimetics—that push the balance further in that direction led to the synergistic killing of cancer cells in culture and the suppression of tumor growth in mouse models of cancer. They also show that a method for screening drugs developed in Letai's lab, BH3 profiling, can be used to identify the BH3 mimetic drug most likely to augment NK cell killing of a given cancer.
More information: Rongqing Pan et al, Augmenting NK cell-based immunotherapy by targeting mitochondrial apoptosis, Cell (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.030