This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Downregulation of angulin-1/LSR induces malignancy in lung adenocarcinoma
A new research paper titled "Downregulation of angulin-1/LSR induces malignancy via upregulation of EGF-dependent claudin-2 and TGF-β-dependent cell metabolism in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells" has been published in Oncotarget.
Abnormal expression of bicellular tight junction claudins, including claudin-2, is observed during carcinogenesis in human lung adenocarcinoma. However, little is known about the role of tricellular tight junction molecule angulin-1/lipolysis-stimulated lipoprotein receptor (LSR).
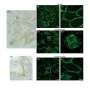
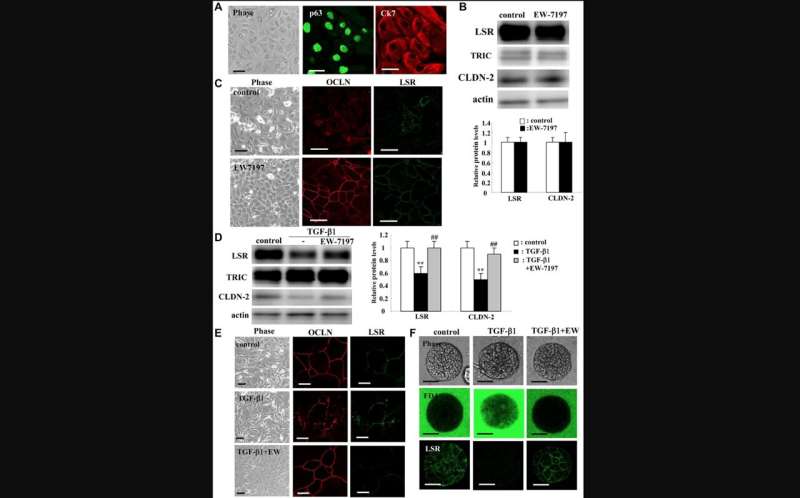
In the present study, researchers Wataru Arai, Takumi Konno, Takayuki Kohno, Yuki Kodera, Mitsuhiro Tsujiwaki, Yuma Shindo, Hirofumi Chiba, Masahiro Miyajima, Yuji Sakuma, Atsushi Watanabe, and Takashi Kojima from Japan's Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine examined expression of claudin-2 in the lung adenocarcinoma tissues and found it was higher than in normal lung tissues, while angulin-1/LSR was poorly or faintly expressed.
"We investigated how loss of angulin-1/LSR affects the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 and normal human lung epithelial (HLE) cells," the researchers write.
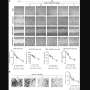
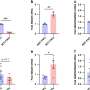
The team found that the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 prevented the increase of claudin-2 expression induced by EGF in A549 cells. Knockdown of LSR induced expression of claudin-2 at the protein and mRNA levels and AG1478 prevented the upregulation of claudin-2 in A549 cells. Knockdown of LSR induced cell proliferation, cell migration and cell metabolism in A549 cells. Knockdown of claudin-2 inhibited the cell proliferation but did not affect the cell migration or cell metabolism of A549 cells.
The TGF-β type I receptor inhibitor EW-7197 prevented the decrease of LSR and claudin-2 induced by TGF-β1 in A549 cells and 2-D culture of normal HLE cells. EW-7197 prevented the increase of cell migration and cell metabolism induced by TGF-β1 in A549 cells. EW-7197 prevented the increase of epithelial permeability of FITC-4kD dextran induced by TGF-β1 in 2.5D culture of normal HLE cells. In conclusion, downregulation of angulin-1/LSR induces malignancy via EGF-dependent claudin-2 and TGF-β-dependent cell metabolism in human lung adenocarcinoma.
"In conclusion, AG1478 and EW-7197 demonstrated potent in vitro anti-lung adenocarcinoma therapeutic activities via LSR/CLDN-2 and the cell metabolism. The use of both AG1478 and EW-7197 may provide a clinical therapeutic approach for lung adenocarcinoma caused by loss of angulin-1/LSR," state the researchers.
More information: Wataru Arai et al, Downregulation of angulin-1/LSR induces malignancy via upregulation of EGF-dependent claudin-2 and TGF-β-dependent cell metabolism in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells, Oncotarget (2023). DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27728