This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Research finds that molecules in vegetables can help to ease lung infection
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that molecules in vegetables like broccoli or cauliflower help to maintain a healthy barrier in the lung and ease infection.
The AHR—aryl hydrocarbon receptor—is a protein found at barrier sites like the gut and the lung. Natural molecules in cruciferous vegetables—for example, kale, cauliflower, broccoli, or cabbage—are dietary 'ligands' for AHR, which means, once eaten, they activate AHR to target a number of genes. Some of the genes targeted switch off the AHR system, allowing it to self-regulate.
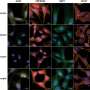
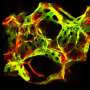
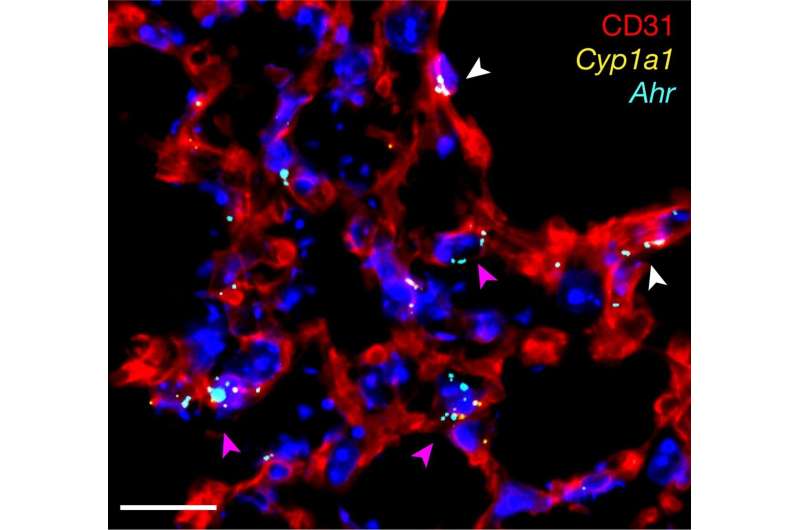
The effect of AHR on immune cells is well understood, but this research, published in Nature, now shows that AHR is also highly active in endothelial cells lining blood vessels in the lung.
The lung barrier between the body and the air outside is only made up of two layers, one of endothelial cells and one of epithelial cells, because it needs to allow oxygen to enter. But the barrier also has to be kept strong against pollution or viruses and bacteria.
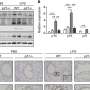
The researchers conducted a series of experiments in mice to show how AHR impacts lung barriers. When mice were infected with the flu virus, blood was found in the airspaces in the lungs, as it had leaked across the damaged barrier. The researchers then showed that AHR was able to prevent the barrier from becoming leaky: when AHR was overactivated they observed less blood in the lung spaces.
They also found that mice with enhanced AHR activity didn't lose as much weight when infected with flu, and were able to better fight off a bacterial infection on top of the original virus.
When AHR was prevented from being expressed in the lung endothelial cells of infected mice, more blood and immune cells were seen in the air spaces, showing greater damage to the barrier.
The researchers also showed that flu infection causes a decrease in protective lung AHR activity, but only in mice fed AHR ligands in their diet before the illness. These findings link food consumption to AHR activity and outcome in viral infection: infected mice didn't eat as much food when ill, so their intake of AHR ligands was reduced and the AHR system was less active, leading to more lung damage.
Despite the infection-driven reduction of AHR activity, it was beneficial for mice to be on an AHR ligand-rich diet: these mice had better barrier integrity and less lung damage during infection than mice on the control diet. These results indicate that AHR has a protective effect on the lung barrier which is impacted by infection, but can be improved by the right diet.
Andreas Wack, Group Leader of the Immunoregulation Laboratory at the Crick, said, "Until recently, we've mainly looked at barrier protection through the lens of immune cells. Now we've shown that AHR is important for maintaining a strong barrier in the lungs through the endothelial cell layer, which is disrupted during infection.
"People may be less likely to maintain a good diet when they're ill, so aren't taking in the molecules from vegetables which make this system work. It's a good idea to eat lots of cruciferous vegetables anyway, but this shows it's even more important to continue eating them when you're ill."
Jack Major, former Ph.D. student in the Wack lab and now visiting scientist at the Crick and first author, said, "What we've identified is a gut-lung axis—linking diet to protection against lung infection via endothelial cells.
"We looked at flu in this research, but other research has shown that COVID-19 may also reduce AHR activity in the lung. It will be interesting to investigate the impact of other respiratory viruses on AHR, and also whether different molecules in our diet use other pathways than AHR to affect lung function via endothelial cells."
Researchers believe AHR may be important in endothelial cells in other barrier organs. A team at MRC and Imperial have reported in Nature that dietary factors activate AHR in the gut endothelial cells, preventing excessive cell reproduction and inflammation.
Similar to the process in the lung, the authors show gut endothelial AHR is important in protection against gut infection. This provides another link between the diet and the state of the gut endothelium, an important contributor to gut health. First author Ben Wiggins has now joined the Immunoregulation Laboratory at the Crick to work with Andreas Wack.
More information: Andreas Wack, Endothelial AHR activity prevents lung barrier disruption in viral infection, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06287-y. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06287-y
Wiggins, B. et al. Endothelial sensing of AHR ligands regulates intestinal homeostasis. Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06508-4