This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New insights into melanoma development and therapy
Malignant melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates from melanocytes or nevi, causing about 80% of skin cancer-related deaths. While some cases have shown significant response to existing molecular targeted therapies, as well as immune checkpoint inhibitors, there are also instances in which these treatments have proven ineffective. Therefore, the development of new therapeutic agents for cases resistant to these drug therapies has been required.
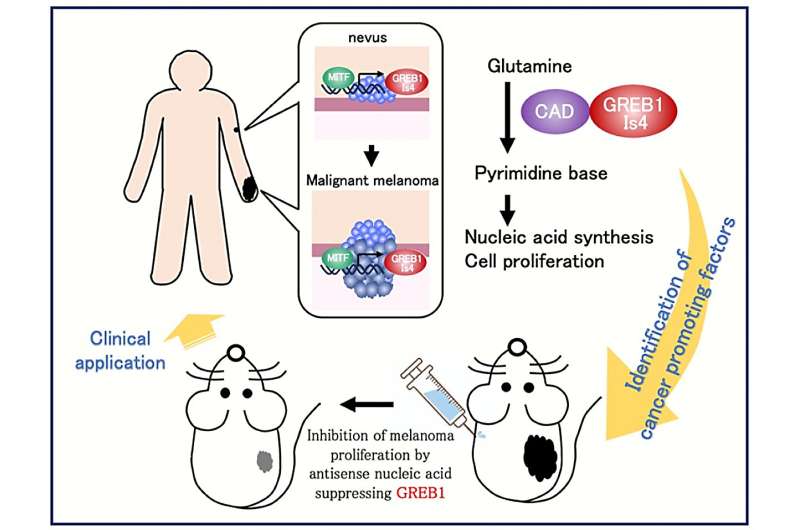
In a study published this month in Oncogene, researchers from Osaka University have discovered that the expression of a specific isoform of GREB1 isoform 4 (Is4) is induced in malignant melanoma cells under the influence of the melanocyte-specific transcription factor, MITF and GREB1 Is4 promotes cancer cell proliferation and the regulation of pyrimidine metabolism. Furthermore, the anti-tumor effect of antisense nucleic acids against GREB1 showed a potential new modality for malignant melanoma.
To investigate the mechanisms by which GREB1 Is4 is induced in malignant melanoma and involved in its growth, the research group used a mouse model of malignant melanoma and human clinical samples to comprehensively demonstrate that induction of GREB1 Is4 expression by the MITF transcription factor is important in malignant melanoma development and prognosis.
Subsequent analysis revealed the pathway by which GREB1 activation leads to melanoma cell proliferation. Generally, cancer cells are characterized by their repeated uncontrolled proliferation, and chemotherapy has traditionally been used to suppress cell proliferation by inhibiting the nucleic acids synthesis.
In this study, the research group demonstrated that CAD, the rate-limiting enzyme for pyrimidine synthesis, as a binding protein for GREB1 Is4, and GREB1 Is4 is essential for pyrimidine synthesis in malignant melanoma by biochemical and metabolomic analyses.
Furthermore, the results of this study are of social significance because GREB1 Is4 has been shown to be a therapeutic target in malignant melanoma, and antisense oligonucleic acids against GREB1 are expected to become new therapeutic agents in the future.
This highly significant study reveals that mechanisms directly responsible for the execution of cell proliferation, such as nucleic acid synthesis, control cancer cell development and proliferation. The results can inform new methods of melanoma treatment in the future.
More information: Koei Shinzawa et al, GREB1 isoform 4 is specifically transcribed by MITF and required for melanoma proliferation, Oncogene (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41388-023-02803-6