This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Exposing hiding lymphoma cells to the immune system
A study led by the group of Didier Trono at EPFL has revealed a crucial survival tactic employed by cancer cells. The scientists have identified a group of proteins, known as "KRAB zinc finger proteins" (KZFPs), that help cancer cells maintain genetic stability and avoid immune system detection. The study is published in Cancer Research.
KZFPs are like managers inside our cells, helping to control which parts of our DNA are switched on or off. For example, some KZFPs interact with transposable elements, which are repetitive DNA sequences constituting more than half of the human genome.
TEs can potentially cause genetic instability if left unchecked, which makes them a threat to cell integrity and immune detection. KZFPs play a crucial role in repressing TEs, ensuring their silent state within heterochromatin, thereby safeguarding genome stability.
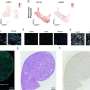
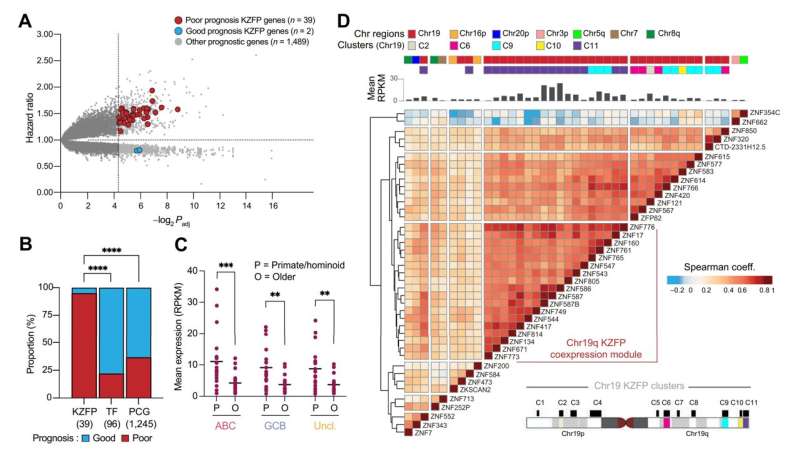
The new study, led by Filipe Martins, a scientist in Trono's group, reveals a correlation between a subset of primate-specific KZFPs and the prognosis of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. The researchers used advanced cell culture techniques, genetic manipulation via short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), and cutting-edge genomic profiling methods to observe the effects of depleting two specific KZFPs in tumor cells from various types of cancers, including Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma.
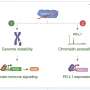
The two proteins to be depleted are known as ZNF587 and ZNF417. They were chosen because they are associated with poor prognosis in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma, but they also target evolutionarily recent transposable elements, which are implicated in genomic stability and immune evasion mechanisms in cancer cells.
Depleting ZNF587 and ZNF417 in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma cells led to significant disruptions in cellular processes. The loss of these proteins resulted in the redistribution of heterochromatin, which created replicative stress, a condition where DNA replication is impeded, which can slow or stall cell division.
This stress triggered an inflammatory response, and enhanced immune system recognition of the cancer cells—it essentially unmasked them and made them visible to the immune system. In fact, the cancer cells showed more diverse neoantigens, which leads to a heightened susceptibility to immune attacks.
"Our study shows that TE regulation and heterochromatin maintenance by KZFPs is essential also in cancer, which allowed us to uncover new functions of KZFPs, previously overlooked in cancer research due to their young evolutionary age and presumed redundancy," explains Didier Trono.
He adds, "Three-quarters of KZFP genes are primate-restricted, challenging the conventional wisdom that the more conserved a protein is, the more essential it should be for cancer development. Our findings indicate that KZFPs not only regulate gene expression but also participate in DNA replication and genome stability, which can influence the genetic diversity and occurrence of subclonal populations of cancer cells, thus playing a pro-oncogenic role."
"This DNA damage and 'viral mimicry' of TEs due to their upregulation led to the activation of cell-intrinsic inflammatory pathways promoting immune rejection in vitro," adds Filipe Martins. "These phenomena have so far been seen only with chemotherapy agents or depletion of cellular enzymes. Therefore, targeting transcription factors holds the promise of a potential immunogenic chemotherapy-like effect."
The findings suggest that cancer cells may exploit these proteins to temper their visibility to immune surveillance. "It is a true conceptual breakthrough," says Trono. "Transposable elements, which most consider only as genetic threats, were revealed to be sentinels against loss of epigenetic controls, and their KZFPs regulators were shown to be subverted by cancer cells to escape this surveillance."
The findings also highlight potential new targets for therapy of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. "The discovery points immediately to novel therapeutic avenues for this disease," says Trono. "It is a line of research for which we are currently raising funds for a large consortium comprising several groups from EPFL in addition to others from Stanford, the Curie Institute, Cornell, the van Andel Institute, and London's Bart Institute, and we are also working towards the launching of a startup."
More information: Olga Rosspopoff et al, A cluster of evolutionarily recent KRAB zinc finger proteins protects cancer cells from replicative stress-induced immunogenic inflammation, Cancer Research (2024). DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1237