This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Sodium channels in breast cancer cells are a promising target for future treatments, study reveals
A study on live tissue cells is the first to reveal how channels that allow sodium to enter into breast cancer cells enable tumors to grow and spread.
The discovery adds to evidence which suggests treating breast cancer patients with sodium channel blockers could be a promising future treatment to prevent the spread of cancer during the gap between diagnosis and surgery.
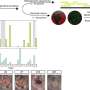
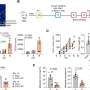
The research team from the universities of York, Cambridge, Nottingham, Aberdeen, Imperial College London and the Institute of Cancer Research, London, looked at tissue samples from more than 1,500 breast cancer patients from the tissue bank of the charity Breast Cancer Now.
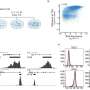
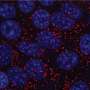
Sodium currents were detected in cells from patients with triple negative breast cancer, an invasive form of the cancer which is difficult to treat because it is missing three of the most effective targets for current treatments.
The findings are published in the journal Oncogene.
More research is needed to establish whether treatments targeting sodium channels in breast cancer tumors would be effective. Previous research by the same scientists has already shown that sodium blockers are an effective treatment in mice and the researchers would now like to carry out a clinical trial.
Around 55,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer every year in the U.K. While many people have successful treatment, about 11,500 die from the disease.
Treatment delays
Senior author of the study, Dr. Will Brackenbury from the Department of Biology at the University of York, said, "Existing sodium blockers are already used to treat conditions such as epilepsy and in dental surgery, so there is a possibility that a drug which already has a good safety profile could be repurposed for breast cancer patients on the waiting list for surgery.
"With delays in access to treatment an increasing area of concern, a treatment option such as this could buy more time for patients of the future.
"With any type of solid cancer, the main reason some people do not get a good outcome is because it has spread, impacting other areas of the body such as the brain, lungs, or bones. Our study provides crucial new insights into how sodium channels can fuel this process in the cells of patients with breast cancer."
Kick off
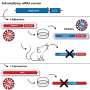
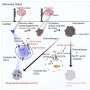
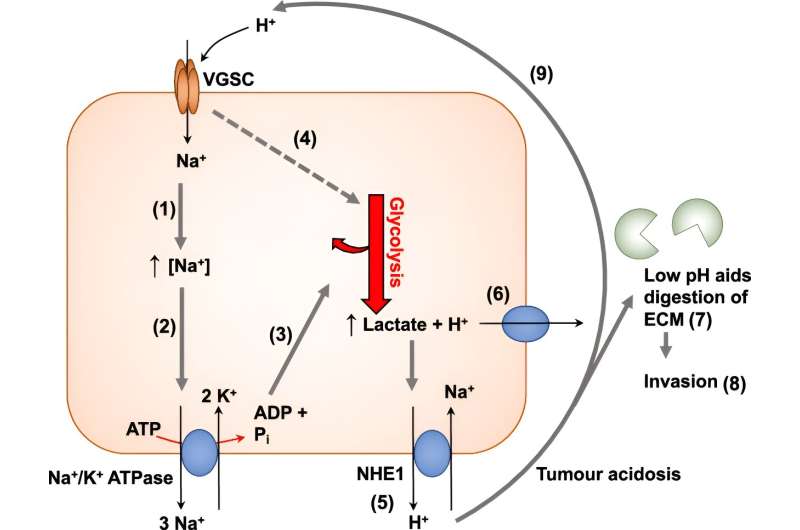
The researchers discovered that "Nav1.5" sodium channels, which sit in the membrane at the surface of the cell, kick off a series of processes in the cell which can enable them to spread out of a tumor.
When sodium enters the cell via these channels, a pump called NKA increases its activity to eject it, like bailing water out of a ship. This uses a lot of energy, which the cell provides through glycolysis or the breakdown of glucose.
In addition to providing energy, this process also produces lactic acid, which is exported out of the cell along with the sodium. This causes the area around the cell to become more acidic, which in turn increases the activities of enzymes which can digest the extracellular matrix—the supportive scaffold that fills the space between cells—freeing up space for the cancer cells to spread and move out of the tumor.
Driving force
As the sodium channel is the driving force that kicks off this process, the researchers hypothesize that blocking them could be an effective way to slow the growth of cancer cells and prevent their spread in breast cancer patients.
The study is also the first large study to confirm that solid breast cancer tumors containing higher levels of the Nav1.5 channel are more likely to metastasize. More research is needed to establish why some tumors have higher levels of this protein than others.
Dr. Simon Vincent, director of research, support and influencing at Breast Cancer Now, said, "This interesting study highlights the significant role of the Nav1.5 protein in helping breast cancer cells spread, which presents a potential new treatment option for breast cancer patients to prevent the disease spreading between diagnosis and surgery.
"Around 61,000 people in the U.K. are living with secondary breast cancer, which is when cancer has spread to other parts of the body and, while treatable, it currently cannot be cured.
"Although more research is needed, the possibility of reducing breast cancer spread with drugs already used safely in the clinic for other conditions is a promising concept and we look forward to seeing future findings."
Dr. Brackenbury added, "There is much more work to be done and many unanswered questions such as why some tumors have more of the protein Nav1.5, and whether there are distinct types of sodium channels in different cancer cells.
"Cancer cells are a bit of a black box, but our study has unraveled a key part of the inner workings of this complex system."
More information: Theresa K. Leslie et al, A novel Nav1.5-dependent feedback mechanism driving glycolytic acidification in breast cancer metastasis, Oncogene (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41388-024-03098-x