Last update:
Medical research news
Medical research
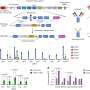
Peptide cocktails show promise in combating antibiotic resistance
Antibiotics are essential tools in modern medicine, regularly used to treat bacterial infections and prevent infections during surgery. However, the widespread use of antibiotics has led to many bacteria developing resistance, ...
3 hours ago
0
0
Medical research
Are AI-chatbots suitable for hospitals? Diagnostic capabilities of large language models tested
Large language models may pass medical exams with flying colors but using them for diagnoses would currently be grossly negligent. Medical chatbots make hasty diagnoses, do not adhere to guidelines, and would put patients' ...
8 hours ago
0
12
Researchers mark milestone in progress toward investigational new drug for triple-negative breast cancer
A new compound developed by researchers at MUSC Hollings Cancer Center shows promise in overcoming chemotherapy resistance in triple-negative breast cancer—and could potentially be applied to fibrotic conditions like liver ...
6 hours ago
0
0

Cure for male pattern baldness given boost by sugar discovery
The key to curing male pattern baldness—a condition that affects up to 50% of men worldwide—could lie in a sugar that naturally occurs in the human body, according to scientists at the University of Sheffield.
6 hours ago
0
2

Scientists identify possible new transmission factor in hospital-acquired Klebsiella infections
Scientists at ADA Forsyth Institute (AFI) have identified a critical factor that may contribute to the spread of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), shedding light on why these infections are so difficult to combat. Their ...
6 hours ago
0
0

Monoclonal antibodies from space: Improved crystallization under microgravity during manufacturing in orbit
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have revolutionized cancer therapy due to their ability to specifically target tumor cells while sparing healthy ones. These biologics have become indispensable in treating various cancers, offering ...
2 hours ago
0
0

Docosahexaenoic acid found to suppress gastric fundus smooth muscle contractions by inhibiting the Orai1 channel
A research group led by Dr. Keisuke Obara, Dr. Kento Yoshioka, and Professor Yoshio Tanaka of the Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Toho University, has found that docosahexaenoic acid ...
2 hours ago
0
0

Neuromuscular training cuts onset of chemo-induced peripheral neuropathy
Neuromuscular training reduces the onset of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), according to a study published online July 1 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
4 hours ago
0
0

Position paper supports inclusion of race and ethnicity in clinical algorithms
A position paper published by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) Working Group on Epidemiology and Quality of Life addresses the ongoing debate about the necessity and impact of incorporating race and ethnicity ...
2 hours ago
0
0

New guideline to improve reporting in precision medicine globally
Ensuring the best reporting in precision medicine research and ultimately the best outcome for patients is the goal of a new international guideline, the first of its kind.
9 hours ago
0
0

Pig transplant research yields a surprise: Bacon safe for some people allergic to red meat
Some people who develop a weird and terrifying allergy to red meat after a bite from a lone star tick can still eat pork from a surprising source: Genetically modified pigs created for organ transplant research.
Jul 21, 2024
0
38

Study finds tumor growth fueled by nucleotide salvage
Cancer cells salvage purine nucleotides to fuel tumor growth, including purines in foods we eat, an important discovery with implications for cancer therapies from research by Children's Medical Center Research Institute ...
Jul 19, 2024
0
20

Study highlights association between urinary and vaginal pathogenic E. coli in recurrent cystitis
The human body hosts a diverse array of microorganisms that maintain a delicate balance crucial for overall health. This microbial harmony can be disrupted by factors such as infections, aging, and hormonal changes, leading ...
Jul 19, 2024
0
0

Detection of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis based on the Stroop-CN model
A paper published in MedComm presented a Chinese EncephalApp diagnosis model (Stroop-CN) based on healthy controls distributed throughout the country and covering different demographic information.
Jul 19, 2024
0
0

Inclusivity needed in patient radiology information systems, review suggests
Outdated and inflexible medical information systems are harmful to transgender and gender diverse (TGD) people, according to a literature review published in the Journal of Medical Radiation Sciences (JMRS). It found patient ...
Jul 19, 2024
0
0

Drug-like molecules show early success in targeting breast cancer brain metastases
Researchers from Drexel's College of Medicine have identified new drugs that show early success in shrinking breast cancer tumors that have metastasized in the brain. The discovery marks the first time that targeting a key ...
Jul 18, 2024
0
0

Climate change may be keeping patients from vital doctor appointments
Temperature extremes, becoming increasingly frequent due to growing global climate change, are associated with higher rates of missed primary care appointments, according to a recently published study by Drexel University ...
Jul 18, 2024
0
0

Hyaluronic acid lip fillers safe for patients with systemic sclerosis, study finds
Thin lips are not only a common cosmetic concern in patients with scleroderma, a condition that involves tightening and hardening of the skin among other effects on internal organs, but also can impact a person's ability ...
Jul 18, 2024
0
0

Federal mandate has improved availability of consent forms for clinical trials, researchers say
A federal regulation called the Common Rule previously requested the public posting of participant consent forms to trials listed in the national clinical study database clinicaltrials.gov, among other human research protections, ...
Jul 18, 2024
0
0

Scientists discover switching off inflammatory protein leads to longer, healthier lifespans in mice
Scientists at the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Medical Science and Imperial College London have discovered that 'switching off' a protein called IL-11 can significantly increase the healthy lifespan of mice by almost ...
Jul 17, 2024
0
444