Malicious brain cell identified—surprising finding fills gap in understanding astrocytes' role in brain disease

Astrocytes—the star-shaped cells of our brain—are very busy. Their job description includes maintaining the blood-brain barrier, removing excess neurotransmitters, repairing brain tissue and more.
Their important role in brain function suggests astrocytes are also involved in disease. Scientists are particularly interested in uncovering how they may drive inflammation in the brain. Brain inflammation is linked to a host of mysterious and devastating diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS), Alzheimer's disease and mental illness. New treatments are urgently needed for these disorders.
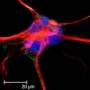
Now, scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP) have identified an astrocyte subpopulation as the dominant cell type to spring into action in vivo (in a living organism) in a neuroinflammatory disease setting. Their early activation inspired their new name: ieAstrocytes (immediate early astrocytes). The study published today in eNeuro.
"There is an urgent need for treatments of brain inflammation disorders that are involved in many diseases, including MS and Alzheimer's disease," says Jerold Chun, M.D., Ph.D., senior author of the paper and professor and senior vice president of Neuroscience Drug Discovery at SBP. "Developing therapies that prevent the formation of ieAstrocytes or reduce their activation levels in the brain could offer new approaches for treating neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases."
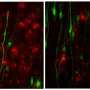
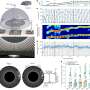
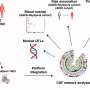
The scientists identified the new type of astrocyte using an unbiased, fluorescent labeling technique to visualize the most active brain cells that express an activity-dependent transcription factor, cFos. Cells that were "turned on" glowed green, allowing the researchers to track activated cells over time and space. Applying this method to a mouse model of brain inflammation allowed visualization of which cells were activated as the disease progressed.
"We expected to see immune cells light up—but surprisingly, they weren't activated. Neither were neurons or microglia," says Chun. "ieAstrocytes were the first and predominant cells activated during disease initiation and progression, suggesting that they are a key gatekeeper and mediator of disease. This is a departure from our previous understanding that astrocytes are spectator cells, only 'moving to the dark side' once initial damage has occurred."
ieAstrocytes increased in number as brain inflammation progressed, indicating they play a key role in disease. Treating the brain cells in an in vivo experiment with a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug for MS, GILENYA (fingolimod), reduced ieAstrocyte formation, further implicating their role in disease and identifying direct brain effects of the drug.
"Greater understanding of ieAstroycytes could unlock more of the brain's mysteries," says Chun. "Defining these cells through their in vivo activity is an important first step, as it can help to guide therapeutic development using a readout that tracks with a brain disease."
Chun's team is already working on their next step: characterizing these astrocytes at the molecular level, particularly the specific genes that are activated.
More information: eNeuro, DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0239-18.2018