How harmless cells can transform into ruthless trained killers
Processes in the human body could turn groups of harmless immune cells into ruthless killers, capable of attacking other cells infected with viruses or parasites, and potentially tumor cells, a new study reveals.
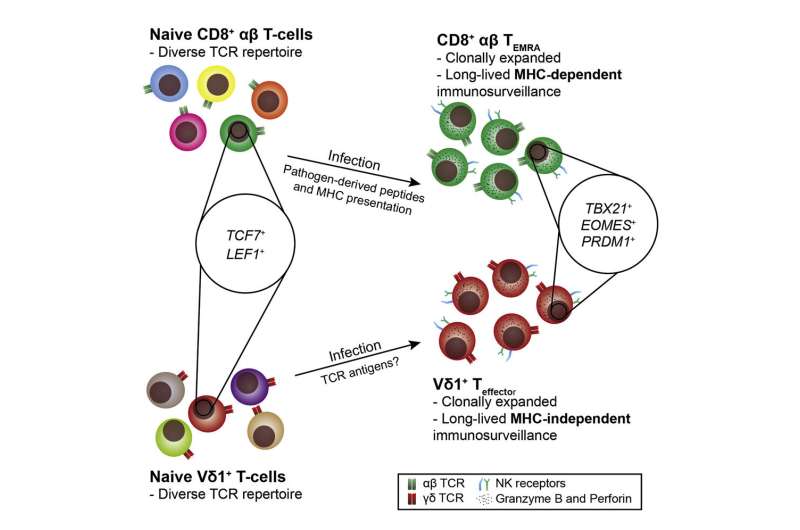
Gamma delta T cells were previously thought to be "pre-programmed" to recognize and destroy other rogue cells, but it now appears there are strong similarities between some types of the cells and well-known "adaptive" subsets of conventional T cells.
An international group of researchers from the UK, Australia, China, Netherlands and U.S.—led by the University of Birmingham—today published its findings in Cell Reports, noting strong similarities to conventional adaptive "killer" T cells.
Senior co-author Professor Ben Willcox, from the University of Birmingham, commented that "human gamma delta T cells have typically been assumed to be pre-programmed, however our study shows that at least in blood, some types mirror the behavior of conventional T cells—suggesting they can be 'trained' to become extremely potent killers once they recognize aberrant target cells—including those infected with viruses, parasites, or possibly tumor cells.
"Our discovery has implications for efforts to develop gamma delta T cells as novel cellular therapies. We hope that it will change the way scientists think about these cells and how they might contribute to the treatment of cancer and infectious disease."
The group examined the profile of gene expression in human gamma delta T cells—showing the cells in a much more "adaptive" light.
Gamma delta cells exist alongside alpha beta T cells and B cells in vertebrates. Researchers have discovered that select human gamma delta T cells appear to transform their pattern of gene expression to activate a "killer" program—dependent on their exposure to abnormal target cells, with successful recognition of such targets likely a key factor triggering this transformation and subsequent attack.
An extremely strong similarity to conventional adaptive killer T cells suggests that the unique contribution of gamma delta T cells is not the type of response they ultimately mount—such as killing a target cell—but that they are able to recognize abnormal target cells in a very different way.
This suggests that they can mount unconventional adaptive responses in situations when conventional adaptive T cells cannot.
Lead author Jack McMurray, from the University of Birmingham, commented that "there are a number of scenarios in which gamma delta T cells may be uniquely suited to respond, due to their unconventional recognition capabilities. These include particular microbial, parasitic and viral infections, and potentially some cancers. Our research provides a basis for ongoing studies to understand how such unconventional adaptive gamma delta T cell responses are triggered, and also for efforts to harness such responses to develop new and more effective treatments for infections and cancer."
More information: Jack L. McMurray et al, Transcriptional profiling of human Vδ1 T cells reveals a pathogen-driven adaptive differentiation program, Cell Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110858