Researchers create new treatment and vaccine for flu and various coronaviruses
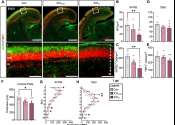
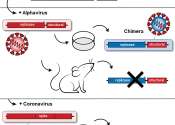
A team of researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered two new ways of preventing and treating respiratory viruses. In back-to-back papers in Nature Communications, the team—from the lab of Navin Varadarajan, ...
8 hours ago
0
38