This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Medical AI tool gets human thumbs-up in first study
A new artificial intelligence computer program created by researchers at the University of Florida and NVIDIA can generate doctors' notes so well that two physicians couldn't tell the difference, according to an early study from both groups.
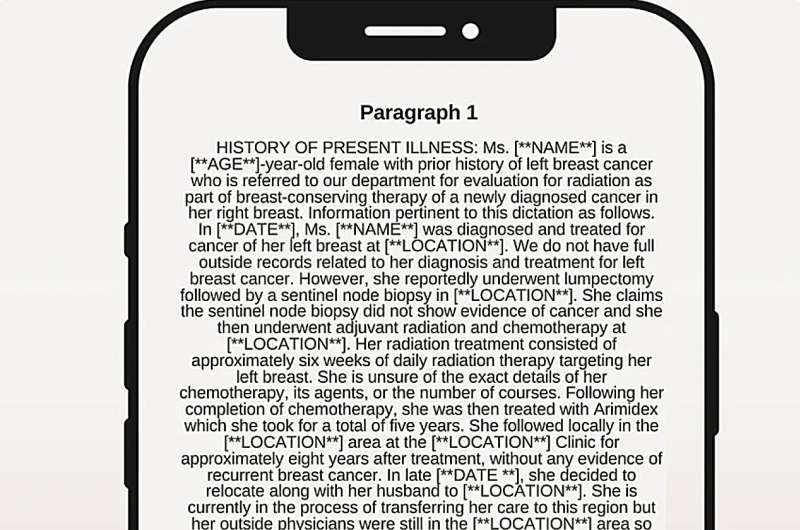
In this proof-of-concept study, physicians reviewed patient notes—some written by actual medical doctors while others were created by the new AI program—and the physicians identified the correct author only 49% of the time.
A team of 19 researchers from NVIDIA and the University of Florida said their findings, published Nov. 16 in the journal npj Digital Medicine, open the door for AI to support health care workers with groundbreaking efficiencies.
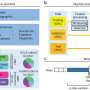
The researchers trained supercomputers to generate medical records based on a new model, GatorTronGPT, that functions similarly to ChatGPT. The free versions of GatorTron models have more than 430,000 downloads from Hugging Face, an open-source AI website. GatorTron models are the site's only models available for clinical research, according to the article's lead author Yonghui Wu, Ph.D., from the UF College of Medicine's department of health outcomes and biomedical informatics.
"In health care, everyone is talking about these models. GatorTron and GatorTronGPT are unique AI models that can power many aspects of medical research and health care. Yet, they require massive data and extensive computing power to build. We are grateful to have this supercomputer, HiPerGator, from NVIDIA to explore the potential of AI in health care," Wu said.
For this research, Wu and his colleagues developed a large language model that allows computers to mimic natural human language. These models work well with standard writing or conversations, but medical records bring additional hurdles, such as needing to protect patients' privacy and being highly technical. Digital medical records cannot be Googled or shared on Wikipedia.
To overcome these obstacles, the researchers stripped UF Health medical records of identifying information from 2 million patients while keeping 82 billion useful medical words. Combining this set with another dataset of 195 billion words, they trained the GatorTronGPT model to analyze the medical data with GPT-3 architecture, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer, a form of neural network architecture. That allowed GatorTronGPT to write clinical text similar to medical doctors' notes.
Here are two paragraphs that reference two patient cases one written by a human and one created by GatorTronGPT—can you tell whether the author was machine or human?
"This GatorTronGPT model is one of the first major products from UF's initiative to incorporate AI across the university. We are so pleased with how the partnership with NVIDIA is already bearing fruit and setting the stage for the future of medicine," said Elizabeth Shenkman, Ph.D., a co-author and chair of UF's department of health outcomes and biomedical informatics.
Of the many possible uses for a medical GPT, one idea involves replacing the tedium of documentation with notes recorded and transcribed by AI. Wu says that UF has an innovation center that is pursuing a commercial version of the software.

For an AI tool to reach such parity with human writing, programmers spend weeks programming supercomputers with clinical vocabulary and language usage based on billions upon billions of words. One resource providing the necessary clinical data is the OneFlorida+ Clinical Research Network, coordinated at UF and representing many health care systems.
"It's critical to have such massive amounts of UF Health clinical data not only available but ready for AI. Only a supercomputer could handle such a big dataset of 277 billion words. We are excited to implement GatorTron and GatorTronGPT models to real-world health care at UF Health," said Jiang Bian, Ph.D., a co-author and UF Health's chief data scientist and chief research information officer.
More information: Cheng Peng et al, A study of generative large language model for medical research and healthcare, npj Digital Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41746-023-00958-w